A simple model for Lutz and Bujard's controllable promoters and its application for analyzing a simple genetic oscillator
- PMID: 25720352
- PMCID: PMC4923745
- DOI: 10.3233/ISB-150465
A simple model for Lutz and Bujard's controllable promoters and its application for analyzing a simple genetic oscillator
Abstract
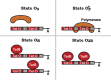
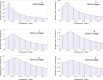
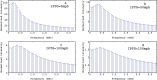
We develop an exact and flexible mathematical model for Lutz and Bujard's controllable promoters. It can be used as a building block for modeling genetic systems based on them. Special attention is paid to deduce all the model parameters from reported (in vitro) experimental data. We validate our model by comparing the regulatory ranges measured in vivo by Lutz and Bujard against the ranges predicted by the model, and which are calculated as the reporter activity obtained under inducing conditions divided by the activity measured under maximal repression. In particular, we verify Bond et al. assertion that the cooperativity between two lac operators can be assumed to be negligible when their central base pairs are separated by 22 or 32 bp [Gene repression by minimal lac loops in vivo, Nucleic Acids Res, 38 (2010) 8072-8082]. Moreover, we also find that the probability that two repressors LacI bind to these operators at the same time can be assumed to be negligible as well. We finally use the model for the promoter P(LlacO-1) to analyze a synthetic genetic oscillator recently build by Stricker et al. [A fast, robust and tunable synthetic gene oscillator, Nature, 456 (2008) 516-519].
Keywords: Synthetic promoters; biochemical oscillations; lac and tet operators.
Figures

References
-
- Expressys: Tools for gene expression, http://www.expressys.com
-
- Elowitz MB, Leibler S. A synthetic oscillatory network of transcriptional regulators. Nature. 2000;403:335–338. - PubMed
-
- Jo J-J, Shin J-S. Construction of intragenic synthetic riboswitches for detection of a small molecule. Biotechnol Lett. 2009;31(10):1577–1581. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

