Activated α2-macroglobulin binding to human prostate cancer cells triggers insulin-like responses
- PMID: 25720493
- PMCID: PMC4392261
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M114.617837
Activated α2-macroglobulin binding to human prostate cancer cells triggers insulin-like responses
Abstract
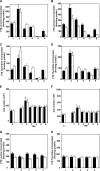
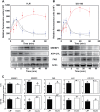
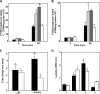
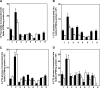
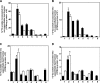
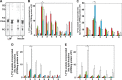
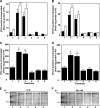
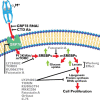
Ligation of cell surface GRP78 by activated α2-macroglobulin (α2M*) promotes cell proliferation and suppresses apoptosis. α2M*-treated human prostate cancer cells exhibit a 2-3-fold increase in glucose uptake and lactate secretion, an effect similar to insulin treatment. In both α2M* and insulin-treated cells, the mRNA levels of SREBP1-c, SREBP2, fatty-acid synthase, acetyl-CoA carboxylase, ATP citrate lyase, and Glut-1 were significantly increased together with their protein levels, except for SREBP2. Pretreatment of cells with α2M* antagonist antibody directed against the carboxyl-terminal domain of GRP78 blocks these α2M*-mediated effects, and silencing GRP78 expression by RNAi inhibits up-regulation of ATP citrate lyase and fatty-acid synthase. α2M* induces a 2-3-fold increase in lipogenesis as determined by 6-[(14)C]glucose or 1-[(14)C]acetate incorporation into free cholesterol, cholesterol esters, triglycerides, free fatty acids, and phosphatidylcholine, which is blocked by inhibitors of fatty-acid synthase, PI 3-kinase, mTORC, or an antibody against the carboxyl-terminal domain of GRP78. We also assessed the incorporation of [(14)CH3]choline into phosphatidylcholine and observed similar effects. Lipogenesis is significantly affected by pretreatment of prostate cancer cells with fatostatin A, which blocks sterol regulatory element-binding protein proteolytic cleavage and activation. This study demonstrates that α2M* functions as a growth factor, leading to proliferation of prostate cancer cells by promoting insulin-like responses. An antibody against the carboxyl-terminal domain of GRP78 may have important applications in prostate cancer therapy.
Keywords: Aerobic Glycolysis; Antibody Directed Against the Carboxyl-terminal Domain of GRP78; Cell Surface GRP78; Glycolysis; Lipogenesis; Prostate Cancer; Signal Transduction; Warburg Effect; α-2-Macroglobulin and Metabolic Regulation.
© 2015 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Inhibition of NF-kappaB1 and NF-kappaB2 activation in prostate cancer cells treated with antibody against the carboxyl terminal domain of GRP78: effect of p53 upregulation.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2010 Feb 19;392(4):538-42. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2010.01.058. Epub 2010 Jan 25. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2010. PMID: 20097177
-
The monomeric receptor binding domain of tetrameric α2-macroglobulin binds to cell surface GRP78 triggering equivalent activation of signaling cascades.Biochemistry. 2013 Jun 11;52(23):4014-25. doi: 10.1021/bi400376s. Epub 2013 May 30. Biochemistry. 2013. PMID: 23721263
-
Activation and cross-talk between Akt, NF-kappaB, and unfolded protein response signaling in 1-LN prostate cancer cells consequent to ligation of cell surface-associated GRP78.J Biol Chem. 2006 May 12;281(19):13694-13707. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M511694200. Epub 2006 Mar 16. J Biol Chem. 2006. PMID: 16543232
-
GRP78 signaling hub a receptor for targeted tumor therapy.Adv Genet. 2010;69:97-114. doi: 10.1016/S0065-2660(10)69006-2. Adv Genet. 2010. PMID: 20807604 Review.
-
Increased lipogenesis in cancer cells: new players, novel targets.Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care. 2006 Jul;9(4):358-65. doi: 10.1097/01.mco.0000232894.28674.30. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care. 2006. PMID: 16778563 Review.
Cited by
-
Cell surface GRP78 promotes tumor cell histone acetylation through metabolic reprogramming: a mechanism which modulates the Warburg effect.Oncotarget. 2017 Nov 14;8(64):107947-107963. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.22431. eCollection 2017 Dec 8. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 29296215 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic significance of alpha-2-macrglobulin and low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein-1 in various cancers.Am J Cancer Res. 2024 Jun 15;14(6):3036-3058. doi: 10.62347/VUJV9180. eCollection 2024. Am J Cancer Res. 2024. PMID: 39005669 Free PMC article.
-
Rh2E2, a novel metabolic suppressor, specifically inhibits energy-based metabolism of tumor cells.Oncotarget. 2016 Mar 1;7(9):9907-24. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.6934. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 26799418 Free PMC article.
-
GRP78 and α2-macroglobulin are new promising targets for metastatic castrate-resistant prostate cancer treatment.Clin Transl Oncol. 2015 Nov;17(11):932-4. doi: 10.1007/s12094-015-1324-9. Epub 2015 Jul 2. Clin Transl Oncol. 2015. PMID: 26133520 No abstract available.
-
Cryo-EM structures reveal the dynamic transformation of human alpha-2-macroglobulin working as a protease inhibitor.Sci China Life Sci. 2022 Dec;65(12):2491-2504. doi: 10.1007/s11427-022-2139-2. Epub 2022 Jun 28. Sci China Life Sci. 2022. PMID: 35781771
References
-
- Jemal A., Thomas A., Murray T., Thun M. (2002) Cancer statistics. CA Cancer J. Clin. 52, 23–47 - PubMed
-
- Abate-Shen C., Shen M. M. (2000) Molecular genetics of prostate cancer. Genes Dev. 14, 2410–2434 - PubMed
-
- Montano X., Djamgoz M. B. (2004) Epidermal growth factor, neurotrophins and the metastatic cascade in prostate cancer. FEBS Lett. 571, 1–8 - PubMed
-
- Schlessinger J. (2000) Cell signaling by receptor tyrosine kinases. Cell 103, 211–225 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

