A comparative planning study of step-and-shoot IMRT versus helical tomotherapy for whole-pelvis irradiation in cervical cancer
- PMID: 25720771
- PMCID: PMC4426928
- DOI: 10.1093/jrr/rrv004
A comparative planning study of step-and-shoot IMRT versus helical tomotherapy for whole-pelvis irradiation in cervical cancer
Abstract
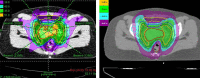
The aim of this study was to compare the dosimetric parameters of whole-pelvis radiotherapy (WPRT) for cervical cancer between step-and-shoot IMRT (SaS-IMRT) and Helical Tomotherapy™ (HT). Retrospective analysis was performed on 20 cervical cancer patients who received WPRT in our center between January 2011 and January 2014. SaS-IMRT and HT treatment plans were generated for each patient. The dosimetric values for target coverage and organ-at-risk (OAR) sparing were compared according to the criteria of the International Commission on Radiation Units and Measurements 83 (ICRU 83) guidelines. Differences in beam-on time (BOT) were also compared. All the PTV dosimetric parameters (D5%, D50% and D95%) for the HT plan were (statistically significantly) of better quality than those for the SaS-IMRT plan (P-value < 0.001 in all respects). HT was also significantly more accurate than SaS-IMRT with respect to the D98% and Dmean of the CTV (P-values of 0.008 and <0.001, respectively). The median Conformity Index (CI) did not differ between the two plans (P-value = 0.057). However, the Uniformity Index for HT was significantly better than that for SaS-IMRT (P-value < 0.001). The median of D50% for the bladder, rectum and small bowel were significantly lower in HT planning than SaS-IMRT (P-value < 0.001). For D2%, we found that HT provided better sparing to the rectum and bladder (P-value < 0.001). However, the median of D2% for the small bowel was comparable for both plans. The median of Dmax of the head of the left femur was significantly lower in the HT plan, but this did not apply for the head of the right femur. BOT for HT was significantly shorter than for SaS-IMRT (P-value < 0.001). HT provided highly accurate plans, with more homogeneous PTV coverage and superior sparing of OARs than SaS-IMRT. In addition, HT enabled a shorter delivery time than SaS-IMRT.
Keywords: IMRT; cervical cancer; step-and-shoot; tomotherapy.
© The Author 2015. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of The Japan Radiation Research Society and Japanese Society for Radiation Oncology.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A dosimetric comparison of tomotherapy and volumetric modulated arc therapy in the treatment of high-risk prostate cancer with pelvic nodal radiation therapy.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2013 Feb 1;85(2):549-54. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2012.03.046. Epub 2012 Jun 5. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2013. PMID: 22677369
-
Assessing the role of volumetric modulated arc therapy (VMAT) relative to IMRT and helical tomotherapy in the management of localized, locally advanced, and post-operative prostate cancer.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2011 Aug 1;80(5):1550-8. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2010.10.024. Epub 2011 May 3. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2011. PMID: 21543164
-
Dosimetric comparisons of helical tomotherapy and step-and-shoot intensity-modulated radiotherapy in nasopharyngeal carcinoma.Radiother Oncol. 2008 Oct;89(1):89-96. doi: 10.1016/j.radonc.2008.05.010. Epub 2008 Jun 2. Radiother Oncol. 2008. PMID: 18524401
-
CTV to PTV in cervical cancer: From static margins to adaptive radiotherapy.Cancer Radiother. 2016 Oct;20(6-7):622-8. doi: 10.1016/j.canrad.2016.07.088. Epub 2016 Sep 7. Cancer Radiother. 2016. PMID: 27614513 Review.
-
[Advances in research on organ-at-risk protection in pelvic tumor external beam radiotherapy].Sheng Wu Yi Xue Gong Cheng Xue Za Zhi. 2024 Jun 25;41(3):627-634. doi: 10.7507/1001-5515.202312073. Sheng Wu Yi Xue Gong Cheng Xue Za Zhi. 2024. PMID: 38932551 Free PMC article. Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
Comparing efficacy of high-dose rate brachytherapy versus helical tomotherapy in the treatment of cervical cancer.J Gynecol Oncol. 2020 Jul;31(4):e42. doi: 10.3802/jgo.2020.31.e42. Epub 2019 Dec 20. J Gynecol Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32026658 Free PMC article.
-
Whole-pelvic radiotherapy with spot-scanning proton beams for uterine cervical cancer: a planning study.J Radiat Res. 2016 Sep;57(5):524-532. doi: 10.1093/jrr/rrw052. Epub 2016 Jul 5. J Radiat Res. 2016. PMID: 27380800 Free PMC article.
-
Dosimetric predictors and Lyman normal tissue complication probability model of hematological toxicity in cervical cancer patients with treated with pelvic irradiation.Med Phys. 2022 Jan;49(1):756-767. doi: 10.1002/mp.15365. Epub 2021 Dec 10. Med Phys. 2022. PMID: 34800297 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ferlay J, Shin H, Bray F, et al. Estimates of worldwide burden of cancer in 2008: GLOBOCAN 2008. Int J Cancer 2010;127:2893–917. - PubMed
-
- Rose PG, Bundy BN, Watkins EB, et al. Concurrent cisplatin-based radiotherapy and chemotherapy for locally advanced cervical cancer. N Engl J Med 1999;340:1144–53. - PubMed
-
- Whitney CW, Sause W, Bundy BN, et al. Randomized comparison of fluorouracil plus cisplatin versus hydroxyurea as an adjunct to radiation therapy in stage IIB–IVA carcinoma of the cervix with negative para-aortic lymph nodes: a Gynecologic Oncology Group and Southwest Oncology Group study. J Clin Oncol 1999;17:1339–48. - PubMed
-
- John M, Flam M, Caplan R, et al. Final results of a phase II chemoradiation protocol for locally advanced cervical cancer: RTOG 85–15. Gynecol Oncol 1996;61:221–6. - PubMed
-
- Tan LT, Zahra M. Long-term survival and late toxicity after chemoradiotherapy for cervical cancer—the Addenbrooke's experience. Clin Oncol 2008;20:358–64. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical