Relation between stroke severity, patient characteristics and CT-perfusion derived blood-brain barrier permeability measurements in acute ischemic stroke
- PMID: 25722019
- PMCID: PMC5131081
- DOI: 10.1007/s00062-015-0375-1
Relation between stroke severity, patient characteristics and CT-perfusion derived blood-brain barrier permeability measurements in acute ischemic stroke
Abstract
Purpose: Increased blood-brain barrier permeability (BBBP) can result from ischemia. In this study the relation between stroke severity, patient characteristics and admission BBBP values measured with CT-perfusion (CTP) was investigated in acute ischemic stroke patients.
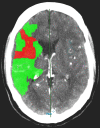
Methods: From prospective data of the Dutch Acute Stroke Study 149 patients with a middle cerebral artery stroke and extended CTP were selected. BBBP values were measured in the penumbra and infarct core as defined by CTP thresholds, and in the contra-lateral hemisphere. The relation between stroke (severity) variables and patient characteristics, including early CT signs, dense vessel sign (DVS), time to scan and National Institute of Health Stroke Score (NIHSS), and BBBP parameters in penumbra and infarct core was quantified with regression analysis.
Results: Early CT signs were related to higher BBBP values in the infarct core (B = 0.710), higher ipsi- to contra-lateral BBBP ratios (B = 0.326) and higher extraction ratios in the infarct core (B = 16.938). Females were found to have lower BBBP values in penumbra and infarct core (B = - 0.446 and - 0.776 respectively) and lower extraction ratios in the infarct core (B = - 10.463). If a DVS was present the ipsi- to contra-lateral BBBP ratios were lower (B = - 0.304). There was no relation between NIHSS or time to scan and BBBP values.
Conclusion: Early CT signs are related to higher BBBP values in the infarct core, suggesting that only severe ischemic damage alters BBBP within the first hours after symptom onset.
Keywords: Acute ischemic stroke; Blood-brain barrier permeability; CT perfusion; Dense vessel sign; Early CT signs.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Computed Tomography Perfusion Derived Blood-Brain Barrier Permeability Does Not Yet Improve Prediction of Hemorrhagic Transformation.Cerebrovasc Dis. 2018;45(1-2):26-32. doi: 10.1159/000485043. Epub 2018 Jan 8. Cerebrovasc Dis. 2018. PMID: 29402765 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamic perfusion-CT assessment of early changes in blood brain barrier permeability of acute ischaemic stroke patients.J Neuroradiol. 2011 Jul;38(3):161-6. doi: 10.1016/j.neurad.2010.08.001. Epub 2010 Oct 14. J Neuroradiol. 2011. PMID: 20950860
-
Optimal duration of acquisition for dynamic perfusion CT assessment of blood-brain barrier permeability using the Patlak model.AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2009 Aug;30(7):1366-70. doi: 10.3174/ajnr.A1592. Epub 2009 Apr 15. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2009. PMID: 19369610 Free PMC article.
-
Imaging viable brain tissue with CT scan during acute stroke.Cerebrovasc Dis. 2004;17 Suppl 3:28-34. doi: 10.1159/000075302. Cerebrovasc Dis. 2004. PMID: 14730256 Review.
-
Perfusion Computed Tomography in Acute Ischemic Stroke.Radiol Clin North Am. 2019 Nov;57(6):1109-1116. doi: 10.1016/j.rcl.2019.06.003. Epub 2019 Jul 30. Radiol Clin North Am. 2019. PMID: 31582038 Review.
Cited by
-
Overexpression of Mitochondrial Ferritin Enhances Blood-Brain Barrier Integrity Following Ischemic Stroke in Mice by Maintaining Iron Homeostasis in Endothelial Cells.Antioxidants (Basel). 2022 Jun 26;11(7):1257. doi: 10.3390/antiox11071257. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35883748 Free PMC article.
-
Post-endovascular treatment, blood-brain barrier disruption, predicts patient outcomes better than pre-treatment status.Neurol Sci. 2024 Sep;45(9):4383-4390. doi: 10.1007/s10072-024-07468-x. Epub 2024 Mar 25. Neurol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38523206
-
Reperfusion facilitates reversible disruption of the human blood-brain barrier following acute ischaemic stroke.Eur Radiol. 2018 Feb;28(2):642-649. doi: 10.1007/s00330-017-5025-3. Epub 2017 Aug 30. Eur Radiol. 2018. PMID: 28856409
-
Permeability Measures Predict Hemorrhagic Transformation after Ischemic Stroke.Ann Neurol. 2020 Sep;88(3):466-476. doi: 10.1002/ana.25785. Epub 2020 Aug 10. Ann Neurol. 2020. PMID: 32418242 Free PMC article.
-
CT Permeability Imaging Predicts Clinical Outcomes in Acute Ischemic Stroke Patients Treated with Intra-arterial Thrombolytic Therapy.Mol Neurobiol. 2017 May;54(4):2539-2546. doi: 10.1007/s12035-016-9838-x. Epub 2016 Mar 18. Mol Neurobiol. 2017. PMID: 26988262
References
-
- Hom J, Dankbaar JW, Soares BP, Schneider T, Cheng SC, Bredno J, Lau BC, Smith W, Dillon WP, Wintermark M. Blood-brain barrier permeability assessed by perfusion ct predicts symptomatic hemorrhagic transformation and malignant edema in acute ischemic stroke. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2011;32(1):41–8. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Wintermark M, Flanders AE, Velthuis B, Meuli R, van Leeuwen M, Goldsher D, Pineda C, Serena J, van der Schaaf I, Waaijer A, Anderson J, Nesbit G, Gabriely I, Medina V, Quiles A, Pohlman S, Quist M, Schnyder P, Bogousslavsky J, Dillon WP, Pedraza S. Perfusion-CT assessment of infarct core and penumbra: receiver operating characteristic curve analysis in 130 patients suspected of acute hemispheric stroke. Stroke. 2006;37(4):979–85. doi: 10.1161/01.STR.0000209238.61459.39. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical