Electrospun silk fibroin nanofibers promote Schwann cell adhesion, growth and proliferation
- PMID: 25722711
- PMCID: PMC4340035
- DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5374.2012.15.008
Electrospun silk fibroin nanofibers promote Schwann cell adhesion, growth and proliferation
Abstract
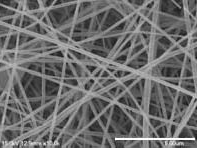
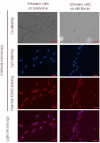
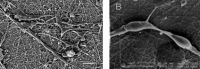
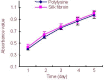
In this study, Schwann cells, at a density of 1 × 10(5) cells/well, were cultured on regenerated silk fibroin nanofibers (305 ± 84 nm) prepared using the electrospinning method. Schwann cells cultured on the silk fibroin nanofibers appeared more ordered, their processes extended further, and they formed more extensive and complex interconnections. In addition, the silk fibroin nanofibers had no impact on the proliferation of Schwann cells or on the secretion of ciliary neurotrophic factor, brain-derived neurotrophic factor or nerve growth factor. These findings indicate that regenerated electrospun silk fibroin nanofibers can promote Schwann cell adhesion, growth and proliferation, and have excellent biocompatibility.
Keywords: Schwann cells; electrospinning; nerve tissue engineering; neural regeneration; peripheral nerve regeneration; silk fibroin.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
Novel conductive polypyrrole/silk fibroin scaffold for neural tissue repair.Neural Regen Res. 2018 Aug;13(8):1455-1464. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.235303. Neural Regen Res. 2018. PMID: 30106059 Free PMC article.
-
Covalent binding of placental derived proteins to silk fibroin improves schwann cell adhesion and proliferation.J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2016 Dec;27(12):188. doi: 10.1007/s10856-016-5783-5. Epub 2016 Nov 5. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2016. PMID: 27817094
-
Biocompatibility evaluation of silk fibroin with peripheral nerve tissues and cells in vitro.Biomaterials. 2007 Mar;28(9):1643-52. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2006.12.004. Epub 2006 Dec 26. Biomaterials. 2007. PMID: 17188747
-
Functionalized silk fibroin nanofibers as drug carriers: Advantages and challenges.J Control Release. 2020 May 10;321:324-347. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2020.02.022. Epub 2020 Feb 13. J Control Release. 2020. PMID: 32061791 Review.
-
Polyurethane/silk fibroin-based electrospun membranes for wound healing and skin substitute applications.Beilstein J Nanotechnol. 2025 Apr 24;16:591-612. doi: 10.3762/bjnano.16.46. eCollection 2025. Beilstein J Nanotechnol. 2025. PMID: 40297246 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Strategies for regeneration of components of nervous system: scaffolds, cells and biomolecules.Regen Biomater. 2015 Mar;2(1):31-45. doi: 10.1093/rb/rbu017. Epub 2015 Jan 13. Regen Biomater. 2015. PMID: 26813399 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A suspended carbon fiber culture to model myelination by human Schwann cells.J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2017 Apr;28(4):57. doi: 10.1007/s10856-017-5867-x. Epub 2017 Feb 16. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2017. PMID: 28210970
-
[Research progress of silk-based biomaterials for peripheral nerve regeneration].Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2024 Sep 15;38(9):1149-1156. doi: 10.7507/1002-1892.202402071. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2024. PMID: 39300893 Free PMC article. Review. Chinese.
-
Schwann cell-matrix coated PCL-MWCNT multifunctional nanofibrous scaffolds for neural regeneration.RSC Adv. 2023 Jan 5;13(2):1392-1401. doi: 10.1039/d2ra05368c. eCollection 2023 Jan 3. RSC Adv. 2023. PMID: 36712918 Free PMC article.
-
Silk fibroin carriers with sustained release capacity for treating neurological diseases.Front Pharmacol. 2023 May 5;14:1117542. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1117542. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37214477 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Jessen KR, Mirsky R. Schwann cells and their precursors emerge as major regulators of nerve development. Trends Neurosci. 1999;22(9):402–410. - PubMed
-
- Singer AJ, Clark RA. Cutaneous wound healing. N Engl J Med. 1999;341(10):738–746. - PubMed
-
- Sendtner M, Holtmann B, Kolbeck R, et al. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor prevents the death of motoneurons in newborn rats after nerve section. Nature. 1992;360(6406):757–759. - PubMed
-
- Höke A, Cheng C, Zochodne DW. Expression of glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor family of growth factors in peripheral nerve injury in rats. Neuroreport. 2000;11(8):1651–1654. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
