Homeostasis, inflammation, and disease susceptibility
- PMID: 25723161
- PMCID: PMC4369762
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2015.02.010
Homeostasis, inflammation, and disease susceptibility
Abstract
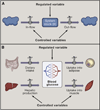
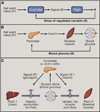
While modernization has dramatically increased lifespan, it has also witnessed the increasing prevalence of diseases such as obesity, hypertension, and type 2 diabetes. Such chronic, acquired diseases result when normal physiologic control goes awry and may thus be viewed as failures of homeostasis. However, while nearly every process in human physiology relies on homeostatic mechanisms for stability, only some have demonstrated vulnerability to dysregulation. Additionally, chronic inflammation is a common accomplice of the diseases of homeostasis, yet the basis for this connection is not fully understood. Here we review the design of homeostatic systems and discuss universal features of control circuits that operate at the cellular, tissue, and organismal levels. We suggest a framework for classification of homeostatic signals that is based on different classes of homeostatic variables they report on. Finally, we discuss how adaptability of homeostatic systems with adjustable set points creates vulnerability to dysregulation and disease. This framework highlights the fundamental parallels between homeostatic and inflammatory control mechanisms and provides a new perspective on the physiological origin of inflammation.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures



References
-
- Åström KJ, Murray RM. Feedback systems: an introduction for scientists and engineers. Princeton: Princeton University Press; 2008.
-
- Badman MK, Pissios P, Kennedy AR, Koukos G, Flier JS, Maratos-Flier E. Hepatic fibroblast growth factor 21 is regulated by PPARalpha and is a key mediator of hepatic lipid metabolism in ketotic states. Cell metabolism. 2007;5:426–437. - PubMed
-
- Barnes BM. Freeze avoidance in a mammal: body temperatures below 0 degree C in an Arctic hibernator. Science. 1989;244:1593–1595. - PubMed
-
- Bateson P, Barker D, Clutton-Brock T, Deb D, D'Udine B, Foley RA, Gluckman P, Godfrey K, Kirkwood T, Lahr MM, et al. Developmental plasticity and human health. Nature. 2004;430:419–421. - PubMed
-
- Bernard C. Paris: J. B. Baillière et fils; 1878. Leçons sur les phénomènes de la vie communs aux animaux et aux végétaux.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

