Analysis of long non-coding RNAs highlights tissue-specific expression patterns and epigenetic profiles in normal and psoriatic skin
- PMID: 25723451
- PMCID: PMC4311508
- DOI: 10.1186/s13059-014-0570-4
Analysis of long non-coding RNAs highlights tissue-specific expression patterns and epigenetic profiles in normal and psoriatic skin
Abstract
Background: Although analysis pipelines have been developed to use RNA-seq to identify long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs), inference of their biological and pathological relevance remains a challenge. As a result, most transcriptome studies of autoimmune disease have only assessed protein-coding transcripts.
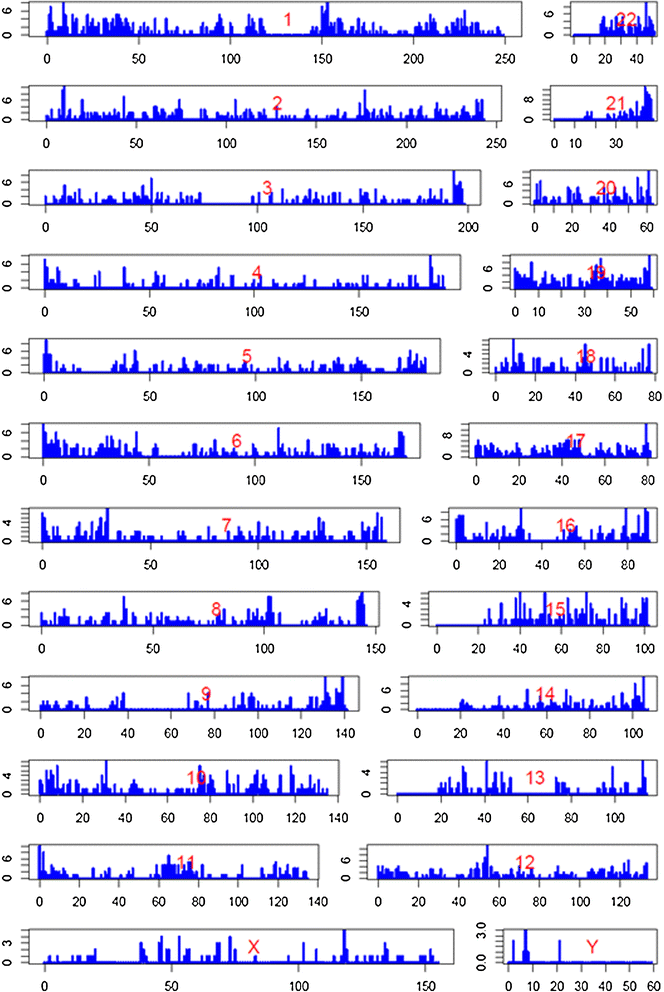
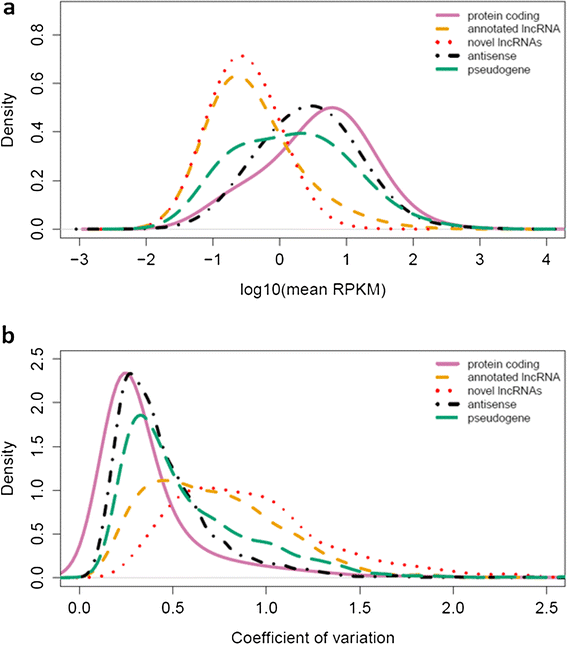
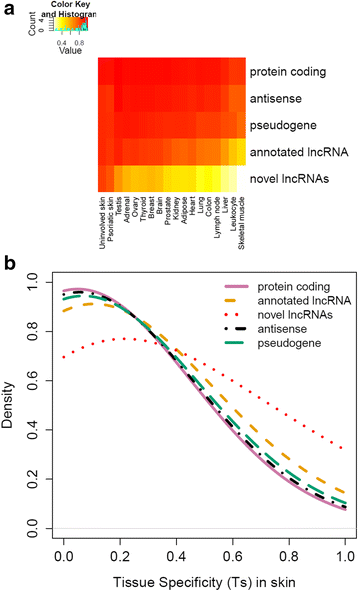
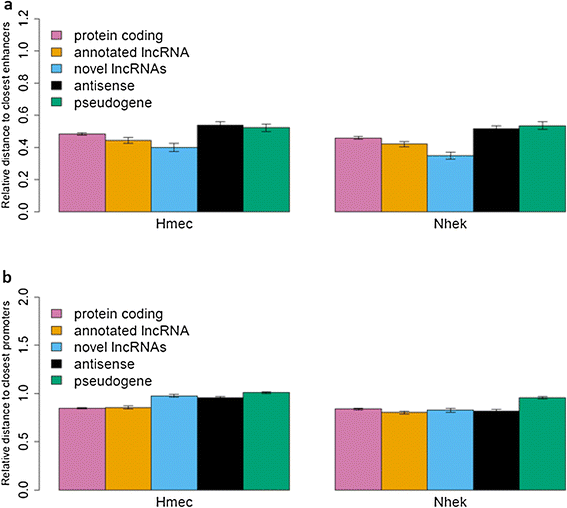
Results: We used RNA-seq data from 99 lesional psoriatic, 27 uninvolved psoriatic, and 90 normal skin biopsies, and applied computational approaches to identify and characterize expressed lncRNAs. We detect 2,942 previously annotated and 1,080 novel lncRNAs which are expected to be skin specific. Notably, over 40% of the novel lncRNAs are differentially expressed and the proportions of differentially expressed transcripts among protein-coding mRNAs and previously-annotated lncRNAs are lower in psoriasis lesions versus uninvolved or normal skin. We find that many lncRNAs, in particular those that are differentially expressed, are co-expressed with genes involved in immune related functions, and that novel lncRNAs are enriched for localization in the epidermal differentiation complex. We also identify distinct tissue-specific expression patterns and epigenetic profiles for novel lncRNAs, some of which are shown to be regulated by cytokine treatment in cultured human keratinocytes.
Conclusions: Together, our results implicate many lncRNAs in the immunopathogenesis of psoriasis, and our results provide a resource for lncRNA studies in other autoimmune diseases.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- K08 AR060802/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR042742/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- AR062382/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- AR054966/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR054966/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR050511/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01EY022005/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM007863/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- Howard Hughes Medical Institute/United States
- R01HG007022/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- AR050511/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR065183/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- AR065183/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR063611/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HG007022/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- AR042742/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EY022005/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

