IVA: accurate de novo assembly of RNA virus genomes
- PMID: 25725497
- PMCID: PMC4495290
- DOI: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btv120
IVA: accurate de novo assembly of RNA virus genomes
Abstract
Motivation: An accurate genome assembly from short read sequencing data is critical for downstream analysis, for example allowing investigation of variants within a sequenced population. However, assembling sequencing data from virus samples, especially RNA viruses, into a genome sequence is challenging due to the combination of viral population diversity and extremely uneven read depth caused by amplification bias in the inevitable reverse transcription and polymerase chain reaction amplification process of current methods.
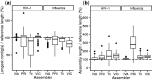
Results: We developed a new de novo assembler called IVA (Iterative Virus Assembler) designed specifically for read pairs sequenced at highly variable depth from RNA virus samples. We tested IVA on datasets from 140 sequenced samples from human immunodeficiency virus-1 or influenza-virus-infected people and demonstrated that IVA outperforms all other virus de novo assemblers.
Availability and implementation: The software runs under Linux, has the GPLv3 licence and is freely available from http://sanger-pathogens.github.io/iva
© The Author 2015. Published by Oxford University Press.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Multiplex Reverse Transcription-PCR for Simultaneous Surveillance of Influenza A and B Viruses.J Clin Microbiol. 2017 Dec;55(12):3492-3501. doi: 10.1128/JCM.00957-17. Epub 2017 Oct 4. J Clin Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28978683 Free PMC article.
-
Viral deep sequencing needs an adaptive approach: IRMA, the iterative refinement meta-assembler.BMC Genomics. 2016 Sep 5;17(1):708. doi: 10.1186/s12864-016-3030-6. BMC Genomics. 2016. PMID: 27595578 Free PMC article.
-
Next generation sequencing for whole genome analysis and surveillance of influenza A viruses.J Clin Virol. 2016 Jun;79:44-50. doi: 10.1016/j.jcv.2016.03.005. Epub 2016 Mar 9. J Clin Virol. 2016. PMID: 27085509
-
How accurate are rapid influenza diagnostic tests?Ann Emerg Med. 2013 Jan;61(1):89-90. doi: 10.1016/j.annemergmed.2012.06.016. Epub 2012 Jul 27. Ann Emerg Med. 2013. PMID: 22841177 Review. No abstract available.
-
RNA virus genomics: a world of possibilities.J Clin Invest. 2009 Sep;119(9):2488-95. doi: 10.1172/JCI38050. J Clin Invest. 2009. PMID: 19729846 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
RNA Sequencing Data Sets and Their Whole-Genome Sequence Assembly of Dengue Virus from Three Serial Passages in Vero Cells.Microbiol Resour Announc. 2021 Apr 29;10(17):e00145-21. doi: 10.1128/MRA.00145-21. Microbiol Resour Announc. 2021. PMID: 33927030 Free PMC article.
-
Validation of Variant Assembly Using HAPHPIPE with Next-Generation Sequence Data from Viruses.Viruses. 2020 Jul 14;12(7):758. doi: 10.3390/v12070758. Viruses. 2020. PMID: 32674515 Free PMC article.
-
Estimating HIV-1 Genetic Diversity in Brazil Through Next-Generation Sequencing.Front Microbiol. 2019 Apr 9;10:749. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.00749. eCollection 2019. Front Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 31024510 Free PMC article.
-
IAVCP (Influenza A Virus Consensus and Phylogeny): Automatic Identification of the Genomic Sequence of the Influenza A Virus from High-Throughput Sequencing Data.Viruses. 2024 May 29;16(6):873. doi: 10.3390/v16060873. Viruses. 2024. PMID: 38932165 Free PMC article.
-
HIV-1 full-genome phylogenetics of generalized epidemics in sub-Saharan Africa: impact of missing nucleotide characters in next-generation sequences.AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 2017 Nov;33(11):1083-1098. doi: 10.1089/AID.2017.0061. Epub 2017 May 25. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 2017. PMID: 28540766 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

