Long Term Effect of High Glucose and Phosphate Levels on the OPG/RANK/RANKL/TRAIL System in the Progression of Vascular Calcification in rat Aortic Smooth Muscle Cells
- PMID: 25729272
- PMCID: PMC4342730
- DOI: 10.4196/kjpp.2015.19.2.111
Long Term Effect of High Glucose and Phosphate Levels on the OPG/RANK/RANKL/TRAIL System in the Progression of Vascular Calcification in rat Aortic Smooth Muscle Cells
Abstract
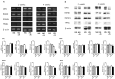
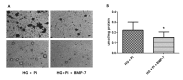
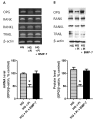
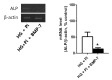
Osteoprotegerin (OPG), receptor activator of NF-κB ligand (RANKL)/receptor activator of NF-κB (RANK) axis, and TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) participate in vascular calcification process including atherosclerosis, but their contributions under high glucose (HG) and phosphate (HP) condition for a long-term period (more than 2 weeks) have not been fully determined. In this study, we evaluated the effects of HG and HP levels over 2 or 4 weeks on the progression of vascular calcification in rat vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs). Calcium deposition in VSMCs was increased in medium containing HG (30 mmol/L D-glucose) with β-glycerophosphate (β-GP, 12 mmol/L) after 2 weeks and increased further after 4 weeks. OPG mRNA and protein expressions were unchanged in HG group with or without β-GP after 2 weeks. However, after 4 weeks, OPG mRNA and protein expressions were significantly lower in HG group with β-GP. No significant expression changes were observed in RANKL, RANK, or TRAIL during the experiment. After 4 weeks of treatment in HG group containing β-GP and rhBMP-7, an inhibitor of vascular calcification, OPG expressions were maintained. Furthermore, mRNA expression of alkaline phosphatase (ALP), a marker of vascular mineralization, was lower in the presence of rhBMP-7. These results suggest that low OPG levels after long term HG and phosphate stimulation might reduce the binding of OPG to RANKL and TRAIL, and these changes could increase osteo-inductive VSMC differentiation, especially vascular mineralization reflected by increased ALP activity during vascular calcification.
Keywords: High glucose; Osteoprotegerin; Phosphate; TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand; Vascular calcification.
Figures

References
-
- Johnson RC, Leopold JA, Loscalzo J. Vascular calcification: pathobiological mechanisms and clinical implications. Circ Res. 2006;99:1044–1059. - PubMed
-
- Shioi A, Nishizawa Y, Jono S, Koyama H, Hosoi M, Morii H. Beta-glycerophosphate accelerates calcification in cultured bovine vascular smooth muscle cells. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 1995;15:2003–2009. - PubMed
-
- Steitz SA, Speer MY, Curinga G, Yang HY, Haynes P, Aebersold R, Schinke T, Karsenty G, Giachelli CM. Smooth muscle cell phenotypic transition associated with calcification: upregulation of Cbfa1 and downregulation of smooth muscle lineage markers. Circ Res. 2001;89:1147–1154. - PubMed
-
- Chen NX, O'Neill KD, Duan D, Moe SM. Phosphorus and uremic serum up-regulate osteopontin expression in vascular smooth muscle cells. Kidney Int. 2002;62:1724–1731. - PubMed
-
- Lehto S, Niskanen L, Suhonen M, Rönnemaa T, Laakso M. Medial artery calcification. A neglected harbinger of cardiovascular complications in non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 1996;16:978–983. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

