Radiologic and clinical outcomes of surgery in high grade spondylolisthesis treated with temporary distraction rod
- PMID: 25729523
- PMCID: PMC4329538
- DOI: 10.4055/cios.2015.7.1.85
Radiologic and clinical outcomes of surgery in high grade spondylolisthesis treated with temporary distraction rod
Abstract
Background: Surgical techniques used in the treatment of patients with high grade lumbar spondylolisthesis (> 50% slippage) are usually associated with a great deal of controversies. We aim to evaluate the surgical outcomes of high grade spondylolisthesis treated with an intraoperative temporary distraction rod.
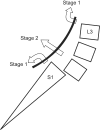
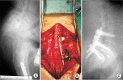
Methods: We retrospectively studied 21 patients (14 females and 7 males), aged 50.4 ± 9.2 years, who had high grade lumbar spondylolisthesis that was treated with intraoperative temporary distraction rods, neural decompression, pedicular screw fixation, and posterolateral fusion involving one more intact upper vertebra. The mean follow-up period was 39.2 months. Radiologic and clinical outcomes were measured by slip angle, slip percentage, correction rate, Oswestry Disability Index (ODI), visual analogue scale (VAS), patient's satisfaction rate in the pre- and postoperative period. Data were analyzed by SPSS ver. 11.5.
Results: Analysis of the preoperative visits and final follow-up visits indicated that surgery could improve ODI, lumbar VAS, and leg VAS from 60.5% to 8.2%, from 6.7 to 2.2, and from 6.9 to 1.3, respectively. Slip angle and slip percentage were also changed from -8° to -15° and from 59.2% to 21.4%, respectively. Mean correction rate at the final follow-up visit was 64.1%. Loss of correction was insignificant and a neurologic complication occurred in one patient due to misplacement of one screw. Excellent and good levels of satisfaction were observed in 90.5% of the patients.
Conclusions: In the surgical treatment of refractory high grade spondylolisthesis, the use of a temporary distraction rod to reduce the slipped vertebra in combination with neural decompression, posterolateral fusion, and longer instrumentation is associated with satisfactory clinical and radiologic outcomes.
Keywords: Radiology; Spondylolisthesis; Surgery; Treatment outcome.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures
References
-
- Meyerding HW. Spondylolisthesis: surgical fusion of lumbosacral portion of spinal column and interarticular facets: use of autogenous bone grafts for relief of disabling backache. J Int Coll Surg. 1956;26(5 Part 1):566–591. - PubMed
-
- Kasliwal MK, Smith JS, Kanter A, et al. Management of high-grade spondylolisthesis. Neurosurg Clin N Am. 2013;24(2):275–291. - PubMed
-
- Klockner C, Weber U. Correction of lumbosacral kyphosis in high grade spondylolisthesis and spondyloptosis. Orthopade. 2001;30(12):983–987. - PubMed
-
- Lengert R, Charles YP, Walter A, Schuller S, Godet J, Steib JP. Posterior surgery in high-grade spondylolisthesis. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2014;100(5):481–484. - PubMed
-
- Hu SS, Bradford DS, Transfeldt EE, Cohen M. Reduction of high-grade spondylolisthesis using Edwards instrumentation. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 1996;21(3):367–371. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

