Hexane Extract of Orthosiphon stamineus Induces Insulin Expression and Prevents Glucotoxicity in INS-1 Cells
- PMID: 25729713
- PMCID: PMC4342537
- DOI: 10.4093/dmj.2015.39.1.51
Hexane Extract of Orthosiphon stamineus Induces Insulin Expression and Prevents Glucotoxicity in INS-1 Cells
Abstract
Background: Hyperglycemia, a characteristic feature of diabetes, induces glucotoxicity in pancreatic β-cells, resulting in further impairment of insulin secretion and worsening glycemic control. Thus, preservation of insulin secretory capacity is essential for the management of type 2 diabetes. In this study, we evaluated the ability of an Orthosiphon stamineus (OS) extract to prevent glucotoxicity in insulin-producing cells.
Methods: We measured insulin mRNA expression and glucose-stimulated insulin secretion (GSIS) in OS-treated INS-1 cells after exposure to a high glucose (HG; 30 mM) concentration.
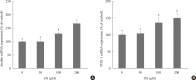
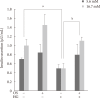
Results: The hexane extract of OS elevated mRNA expression of insulin as well as pancreatic and duodenal homeobox-1 of INS-1 cells in a dose-dependent manner. The hexane OS extract also increased the levels of phosphorylated phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K) in a concentration-dependent manner. Additionally, Akt phosphorylation was elevated by treatment with 100 and 200 µmol of the hexane OS extract. Three days of HG exposure suppressed insulin mRNA expression and GSIS; these expressions were restored by treatment with the hexane OS extract. HG elevated peroxide levels in the INS-1 cells. These levels were unaffected by OS treatment under both normal and hyperglycemic conditions.
Conclusion: Our results suggested that the hexane extract of OS elevates insulin mRNA expression and prevents glucotoxicity induced by a 3-day treatment with HG. This was associated with the activation of PI-3K and Akt.
Keywords: Glucose-stimulated insulin secretion, Insulin mRNA; Glucotoxicity; Orthosiphon stamineus.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Inhibition of fatty acid translocase cluster determinant 36 (CD36), stimulated by hyperglycemia, prevents glucotoxicity in INS-1 cells.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2012 Apr 6;420(2):462-6. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2012.03.020. Epub 2012 Mar 10. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2012. PMID: 22430143
-
Melatonin prevents pancreatic β-cell loss due to glucotoxicity: the relationship between oxidative stress and endoplasmic reticulum stress.J Pineal Res. 2014 Mar;56(2):143-53. doi: 10.1111/jpi.12106. Epub 2013 Nov 25. J Pineal Res. 2014. PMID: 24168371
-
Glucotoxicity in the INS-1 rat insulinoma cell line is mediated by the orphan nuclear receptor small heterodimer partner.Diabetes. 2007 Feb;56(2):431-7. doi: 10.2337/db06-0753. Diabetes. 2007. PMID: 17259388
-
Antidiabetic properties and mechanism of action of Orthosiphon stamineus Benth bioactive sub-fraction in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats.J Acupunct Meridian Stud. 2013 Feb;6(1):31-40. doi: 10.1016/j.jams.2013.01.005. Epub 2013 Feb 6. J Acupunct Meridian Stud. 2013. PMID: 23433053
-
Saponins of Momordica charantia increase insulin secretion in INS-1 pancreatic β-cells via the PI3K/Akt/FoxO1 signaling pathway.Endocrinol Diabetes Nutr (Engl Ed). 2021 May;68(5):329-337. doi: 10.1016/j.endinu.2020.05.005. Epub 2020 Oct 15. Endocrinol Diabetes Nutr (Engl Ed). 2021. PMID: 33069631 English, Spanish.
Cited by
-
A Systematic Review of Orthosiphon stamineus Benth. in the Treatment of Diabetes and Its Complications.Molecules. 2022 Jan 10;27(2):444. doi: 10.3390/molecules27020444. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 35056765 Free PMC article.
-
Understanding glycaemic control and current approaches for screening antidiabetic natural products from evidence-based medicinal plants.Plant Methods. 2019 Sep 7;15:105. doi: 10.1186/s13007-019-0487-8. eCollection 2019. Plant Methods. 2019. PMID: 31516543 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Short-Term Protocols to Obtain Insulin-Producing Cells from Rat Adipose Tissue: Signaling Pathways and In Vivo Effect.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 May 18;20(10):2458. doi: 10.3390/ijms20102458. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31109026 Free PMC article.
-
Can Tea Extracts Exert a Protective Effect Against Diabetes by Reducing Oxidative Stress and Decreasing Glucotoxicity in Pancreatic β-Cells?Diabetes Metab J. 2015 Feb;39(1):27-30. doi: 10.4093/dmj.2015.39.1.27. Diabetes Metab J. 2015. PMID: 25729709 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Poitout V, Robertson RP. Minireview: secondary beta-cell failure in type 2 diabetes: a convergence of glucotoxicity and lipotoxicity. Endocrinology. 2002;143:339–342. - PubMed
-
- Kim YW, Moon JS, Seo YJ, Park SY, Kim JY, Yoon JS, Lee IK, Lee HW, Won KC. Inhibition of fatty acid translocase cluster determinant 36 (CD36), stimulated by hyperglycemia, prevents glucotoxicity in INS-1 cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2012;420:462–466. - PubMed
-
- Ashcroft FM, Gribble FM. ATP-sensitive K+ channels and insulin secretion: their role in health and disease. Diabetologia. 1999;42:903–919. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

