Hexane Extract of Orthosiphon stamineus Induces Insulin Expression and Prevents Glucotoxicity in INS-1 Cells
- PMID: 25729713
- PMCID: PMC4342537
- DOI: 10.4093/dmj.2015.39.1.51
Hexane Extract of Orthosiphon stamineus Induces Insulin Expression and Prevents Glucotoxicity in INS-1 Cells
Abstract
Background: Hyperglycemia, a characteristic feature of diabetes, induces glucotoxicity in pancreatic β-cells, resulting in further impairment of insulin secretion and worsening glycemic control. Thus, preservation of insulin secretory capacity is essential for the management of type 2 diabetes. In this study, we evaluated the ability of an Orthosiphon stamineus (OS) extract to prevent glucotoxicity in insulin-producing cells.
Methods: We measured insulin mRNA expression and glucose-stimulated insulin secretion (GSIS) in OS-treated INS-1 cells after exposure to a high glucose (HG; 30 mM) concentration.
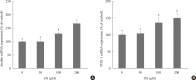
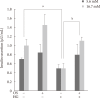
Results: The hexane extract of OS elevated mRNA expression of insulin as well as pancreatic and duodenal homeobox-1 of INS-1 cells in a dose-dependent manner. The hexane OS extract also increased the levels of phosphorylated phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K) in a concentration-dependent manner. Additionally, Akt phosphorylation was elevated by treatment with 100 and 200 µmol of the hexane OS extract. Three days of HG exposure suppressed insulin mRNA expression and GSIS; these expressions were restored by treatment with the hexane OS extract. HG elevated peroxide levels in the INS-1 cells. These levels were unaffected by OS treatment under both normal and hyperglycemic conditions.
Conclusion: Our results suggested that the hexane extract of OS elevates insulin mRNA expression and prevents glucotoxicity induced by a 3-day treatment with HG. This was associated with the activation of PI-3K and Akt.
Keywords: Glucose-stimulated insulin secretion, Insulin mRNA; Glucotoxicity; Orthosiphon stamineus.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures



References
-
- Poitout V, Robertson RP. Minireview: secondary beta-cell failure in type 2 diabetes: a convergence of glucotoxicity and lipotoxicity. Endocrinology. 2002;143:339–342. - PubMed
-
- Kim YW, Moon JS, Seo YJ, Park SY, Kim JY, Yoon JS, Lee IK, Lee HW, Won KC. Inhibition of fatty acid translocase cluster determinant 36 (CD36), stimulated by hyperglycemia, prevents glucotoxicity in INS-1 cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2012;420:462–466. - PubMed
-
- Ashcroft FM, Gribble FM. ATP-sensitive K+ channels and insulin secretion: their role in health and disease. Diabetologia. 1999;42:903–919. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

