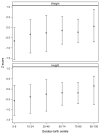
Relation between birth weight and weight and height at the age of 2 in children born preterm
- PMID: 25730133
- PMCID: PMC4485423
- DOI: 10.1055/s-0035-1544947
Relation between birth weight and weight and height at the age of 2 in children born preterm
Abstract
Objective: The aim of the study was to evaluate associations between fetal growth and weight at 2 years in infants born preterm using a customized approach for birth weight.
Study design: This is a secondary analysis of a multicenter trial that included a 2-year follow-up of children born prematurely. Customized birth weight percentiles were calculated using the Gardosi model for a U.S. population, and the relation between customized percentile and weight and height at 2 years (adjusted for gender using z-score) was determined using regression analysis and by comparing z-scores for children with birth weight <10th versus ≥10th percentile.
Results: Weight z-score at 2 years was significantly lower in the <10th than in the ≥10th percentile group (median [interquartile range, IQR]: -0.66 [-1.58, -0.01] vs. -0.23 [-1.05, 0.55]; p < 0.001), and remained after adjusting for maternal education (p < 0.001). A similar relationship was noted for height z-score between groups (median [IQR]: -0.56 [-1.29, 0.19] vs. -0.24 [-0.99, 0.37]; p < 0.001). Positive relationships between customized birth weight percentile and weight and height at 2 years were noted (p < 0.001 for both), but were not strong (R (2) = 0.04 and 0.02, respectively).
Conclusion: Customized birth weight percentile is a minor determinant of weight at 2 years among children born preterm.
Thieme Medical Publishers 333 Seventh Avenue, New York, NY 10001, USA.
Figures
References
-
- McIntire D, Bloom SL, Casey B, Leveno KJ. Birth weight in relation to morbidity and mortality among newborn infants. N Engl J Med. 1999;340:1234–1238. - PubMed
-
- Hediger ML, Overpeck MD, Maurer KR, et al. Growth of infants and young children born small or large for gestational age. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med. 1998;152:1225–12331. - PubMed
-
- Freedman DS, Mei Z, Srinivasan SR, Berenson GS, Dietz WH. Cardiovascular risk factors and excess adiposity among overweight children and adolescents: the Bogalusa Heart Study. J Pediatr. 2007;150:12–7. - PubMed
-
- Ozanne SE, Fernandez-Twinn D, Hales CN. Fetal growth and adult diseases. Sem Perinat. 2004;28:81–87. - PubMed
-
- Barker DJ, Osmond C, Forsen TJ, Kajantie E, Eriksson JG. Trajectories of growth among children who have coronary events as adults. N Engl J Med. 2005;353:1802–1809. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- HD36801/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 HD027869/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD040544/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD034136/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD040485/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- HD40485/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD040560/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HD019897/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD040512/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HD036801/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD040500/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- HD27861/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 HD034116/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- HD27869/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- HD34136/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 HD040560/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- HD27860/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 HD027915/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- HD21414/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD027905/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- HD40512/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 HD040544/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 HD034208/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 HD040512/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- HD40545/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD034116/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- HD40560/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- MO1-RR-000080/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- HD53907/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- HD34210/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- HD21410/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD027869/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD027917/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- HD34116/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD034122/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD027915/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 HD040545/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 HD040485/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD027860/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- HD40500/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD034208/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD053097/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- HD34208/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- HD27915/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 HD040500/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- HD27917/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- P2C HD050924/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD021410/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD036801/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000080/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U24 HD036801/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD040545/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- HD40544/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical