Rare variants in neuronal excitability genes influence risk for bipolar disorder
- PMID: 25730879
- PMCID: PMC4371952
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1424958112
Rare variants in neuronal excitability genes influence risk for bipolar disorder
Abstract
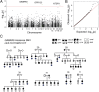
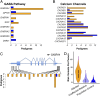
We sequenced the genomes of 200 individuals from 41 families multiply affected with bipolar disorder (BD) to identify contributions of rare variants to genetic risk. We initially focused on 3,087 candidate genes with known synaptic functions or prior evidence from genome-wide association studies. BD pedigrees had an increased burden of rare variants in genes encoding neuronal ion channels, including subunits of GABAA receptors and voltage-gated calcium channels. Four uncommon coding and regulatory variants also showed significant association, including a missense variant in GABRA6. Targeted sequencing of 26 of these candidate genes in an additional 3,014 cases and 1,717 controls confirmed rare variant associations in ANK3, CACNA1B, CACNA1C, CACNA1D, CACNG2, CAMK2A, and NGF. Variants in promoters and 5' and 3' UTRs contributed more strongly than coding variants to risk for BD, both in pedigrees and in the case-control cohort. The genes and pathways identified in this study regulate diverse aspects of neuronal excitability. We conclude that rare variants in neuronal excitability genes contribute to risk for BD.
Keywords: GABAA receptor; bipolar disorder; family genomics; regulatory variants; voltage-gated calcium channel.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Goodwin FK, Jamison KR. Manic-Depressive Illness: Bipolar Disorders and Recurrent Depression. Oxford Univ Press; Oxford: 2007.
-
- Merikangas KR, Low NCP. The epidemiology of mood disorders. Curr Psychiatry Rep. 2004;6(6):411–421. - PubMed
-
- Craddock N, Sklar P. Genetics of bipolar disorder. Lancet. 2013;381(9878):1654–1662. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- R01 MH059556/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- MH059556/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- MH59533/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH059567/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH059545/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- MH59553/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH059548/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH059534/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- MH59545/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- MH60068/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- MH59567/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- P50CA89392/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH059553/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH060068/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH059535/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- MH059534/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- 5K02DA021237/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA089392/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- Z01 MH002810/ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- 1Z01MH002810-01/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- MH059548/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001108/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH059533/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- P50 GM076547/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- MH59535/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- K02 DA021237/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH094483/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

