FAAH genetic variation enhances fronto-amygdala function in mouse and human
- PMID: 25731744
- PMCID: PMC4351757
- DOI: 10.1038/ncomms7395
FAAH genetic variation enhances fronto-amygdala function in mouse and human
Abstract
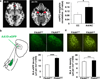
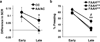
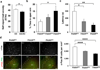
Cross-species studies enable rapid translational discovery and produce the broadest impact when both mechanism and phenotype are consistent across organisms. We developed a knock-in mouse that biologically recapitulates a common human mutation in the gene for fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH) (C385A; rs324420), the primary catabolic enzyme for the endocannabinoid anandamide. This common polymorphism impacts the expression and activity of FAAH, thereby increasing anandamide levels. Here, we show that the genetic knock-in mouse and human variant allele carriers exhibit parallel alterations in biochemisty, neurocircuitry and behaviour. Specifically, there is reduced FAAH expression associated with the variant allele that selectively enhances fronto-amygdala connectivity and fear extinction learning, and decreases anxiety-like behaviours. These results suggest a gain of function in fear regulation and may indicate for whom and for what anxiety symptoms FAAH inhibitors or exposure-based therapies will be most efficacious, bridging an important translational gap between the mouse and human.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- MH079513/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- GM07739/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P50 MH079513/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- EY007138/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS052819/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- Canadian Institutes of Health Research/Canada
- MH060478/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- NS052819/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- DA017259/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- P01 DA017259/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- T32 EY007138/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM007739/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R25 MH060478/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

