A social chemosignaling function for human handshaking
- PMID: 25732039
- PMCID: PMC4345842
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.05154
A social chemosignaling function for human handshaking
Abstract
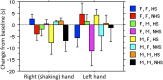
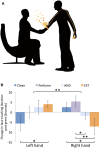
Social chemosignaling is a part of human behavior, but how chemosignals transfer from one individual to another is unknown. In turn, humans greet each other with handshakes, but the functional antecedents of this behavior remain unclear. To ask whether handshakes are used to sample conspecific social chemosignals, we covertly filmed 271 subjects within a structured greeting event either with or without a handshake. We found that humans often sniff their own hands, and selectively increase this behavior after handshake. After handshakes within gender, subjects increased sniffing of their own right shaking hand by more than 100%. In contrast, after handshakes across gender, subjects increased sniffing of their own left non-shaking hand by more than 100%. Tainting participants with unnoticed odors significantly altered the effects, thus verifying their olfactory nature. Thus, handshaking may functionally serve active yet subliminal social chemosignaling, which likely plays a large role in ongoing human behavior.
Keywords: handshaking; human; neuroscience; pheromones; sniffing; social chemosignaling.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- Achiraman S, Archunan G, Abirami B, Kokilavani P, Suriyakalaa U, SankarGanesh D, Kamalakkannan S, Kannan S, Habara Y, Sankar R. Increased squalene concentrations in the clitoral gland during the estrous cycle in rats: an estrus-indicating scent mark? Theriogenology. 2011;76:1676–1683. doi: 10.1016/j.theriogenology.2011.06.033. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bensafi M, Brown WM, Tsutsui T, Mainland JD, Johnson BN, Bremner EA, Young N, Mauss I, Ray B, Gross J, Richards J, Stappen I, Levenson RW, Sobel N. Sex-steroid derived compounds induce sex-specific effects on autonomic nervous system function in humans. Behavioral Neuroscience. 2003;117:1125–1134. doi: 10.1037/0735-7044.117.6.1125. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

