Polyphosphoinositide binding domains: Key to inositol lipid biology
- PMID: 25732852
- PMCID: PMC4380703
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2015.02.013
Polyphosphoinositide binding domains: Key to inositol lipid biology
Erratum in
- Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015 Sep;1851(9):1283
Abstract
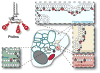
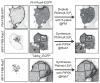
Polyphosphoinositides (PPIn) are an important family of phospholipids located on the cytoplasmic leaflet of eukaryotic cell membranes. Collectively, they are critical for the regulation of many aspects of membrane homeostasis and signaling, with notable relevance to human physiology and disease. This regulation is achieved through the selective interaction of these lipids with hundreds of cellular proteins, and thus the capability to study these localized interactions is crucial to understanding their functions. In this review, we discuss current knowledge of the principle types of PPIn-protein interactions, focusing on specific lipid-binding domains. We then discuss how these domains have been re-tasked by biologists as molecular probes for these lipids in living cells. Finally, we describe how the knowledge gained with these probes, when combined with other techniques, has led to the current view of the lipids' localization and function in eukaryotes, focusing mainly on animal cells. This article is part of a Special Issue entitled Phosphoinositides.
Keywords: Fluorescence imaging; Membrane; PH-domain; PX-domain; Phosphoinositide; Phospholipase C.
Published by Elsevier B.V.
Figures
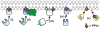

References
-
- Lemmon M. Phosphoinositide recognition domains. Traffic. 2003;4:201–213. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

