Burden of Serious Infections in Adults With Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: A National Population-Based Study, 1996-2011
- PMID: 25732901
- PMCID: PMC4516647
- DOI: 10.1002/acr.22575
Burden of Serious Infections in Adults With Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: A National Population-Based Study, 1996-2011
Abstract
Objective: To compare rates of hospitalization for serious infections, trends in rates from 1996 to 2011, and in-hospital mortality between patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and those without SLE in a national sample.
Methods: We analyzed hospitalizations for pneumonia, bacteremia/sepsis, urinary tract infections, skin infections, and opportunistic infections among adults in the Nationwide Inpatient Sample. We compared rates of hospitalization yearly among patients with SLE and the general population. We also computed odds ratios (ORs) for in-hospital mortality.
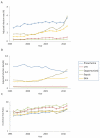
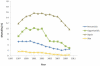
Results: In 1996, the estimated number of hospitalizations for pneumonia in patients with SLE was 4,382, followed by sepsis (2,305), skin infections (1,422), urinary tract infections (643), and opportunistic infections (370). Rates were much higher in patients with SLE than in those without SLE, with age-adjusted relative risks ranging from 5.7 (95% confidence interval [95% CI] 5.5-6.0) for pneumonia to 9.8 (95% CI 9.1-10.7) for urinary tract infection in 1996. Risks increased over time, so that by 2011, all relative risks exceeded 12.0. Overall risk of in-hospital mortality was higher in SLE only for opportunistic infections (adjusted OR 1.52 [95% CI 1.12-2.07]). However, in pneumonia and sepsis, mortality risks were higher in SLE among those who required mechanical ventilation.
Conclusion: Hospitalization rates for serious infections in SLE increased substantially between 1996 and 2011, reaching over 12 times higher than in patients without SLE in 2011. Reasons for this acceleration are unclear. In-hospital mortality was higher among patients with SLE and opportunistic infections and those with pneumonia or sepsis who required mechanical ventilation.
© 2015, American College of Rheumatology.
Figures

Comment in
-
Connective tissue diseases: The burden of serious infections in SLE.Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2015 Jun;11(6):326-7. doi: 10.1038/nrrheum.2015.55. Epub 2015 Apr 21. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2015. PMID: 25900209 No abstract available.
References
-
- Lee J, Dhillon N, Pope J. All-cause hospitalizations in systemic lupus erythematosus from a large Canadian referral centre. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2013;52:905–9. - PubMed
-
- Goldblatt F, Chambers S, Rahman A, Isenberg DA. Serious infections in British patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: hospitalisations and mortality. Lupus. 2009;18:682–9. - PubMed
-
- Edwards CJ, Lian TY, Badsha H, Teh CL, Arden N, Chng HH. Hospitalization of individuals with systemic lupus erythematosus: characteristics and predictors of outcome. Lupus. 2003;12:672–6. - PubMed
-
- Gladman DD, Hussain F, Ibanez D, Urowitz MB. The nature and outcome of infection in systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus. 2002;11:234–9. - PubMed
-
- Petri M, Genovese M. Incidence of and risk factors for hospitalizations in systemic lupus erythematosus: a prospective study of the Hopkins Lupus Cohort. J Rheumatol. 1992;19:1559–65. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

