Dose-intensified chemotherapy alone or in combination with mogamulizumab in newly diagnosed aggressive adult T-cell leukaemia-lymphoma: a randomized phase II study
- PMID: 25733162
- PMCID: PMC5024033
- DOI: 10.1111/bjh.13338
Dose-intensified chemotherapy alone or in combination with mogamulizumab in newly diagnosed aggressive adult T-cell leukaemia-lymphoma: a randomized phase II study
Abstract
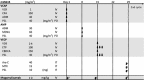
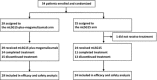
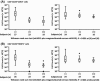
This multicentre, randomized, phase II study was conducted to examine whether the addition of mogamulizumab, a humanized anti-CC chemokine receptor 4 antibody, to mLSG15, a dose-intensified chemotherapy, further increases efficacy without compromising safety of patients with newly diagnosed aggressive adult T-cell leukaemia-lymphoma (ATL). Patients were assigned 1:1 to receive mLSG15 plus mogamulizumab or mLSG15 alone. The primary endpoint was the complete response rate (%CR); secondary endpoints included the overall response rate (ORR) and safety. The %CR and ORR in the mLSG15-plus-mogamulizumab arm (n = 29) were 52% [95% confidence interval (CI), 33-71%] and 86%, respectively; the corresponding values in the mLSG15 arm (n = 24) were 33% (95% CI, 16-55%) and 75%, respectively. Grade ≥ 3 treatment-emergent adverse events, including anaemia, thrombocytopenia, lymphopenia, leucopenia and decreased appetite, were observed more frequently (≥10% difference) in the mLSG15-plus-mogamulizumab arm. Several adverse events, including skin disorders, cytomegalovirus infection, pyrexia, hyperglycaemia and interstitial lung disease, were observed only in the mLSG15-plus-mogamulizumab arm. Although the combination strategy showed a potentially less favourable safety profile, a higher %CR was achieved, providing the basis for further investigation of this novel treatment for newly diagnosed aggressive ATL. This study was registered at ClinicalTrials.gov, identifier: NCT01173887.
Keywords: CCR4; adult T-cell leukaemia-lymphoma; antibody therapy; mogamulizumab; randomized phase II study.
© 2015 The Authors. British Journal of Haematology published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures

References
-
- Chihara, D. , Ito, H. , Matsuda, T. , Katanoda, K. , Shibata, A. , Taniguchi, S. , Utsunomiya, A. , Sobue, T. & Matsuo, K. (2013) Association between decreasing trend in the mortality of adult T‐cell leukemia/lymphoma and allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplants in Japan: analysis of Japanese vital statistics and Japan Society for Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation (JSHCT). Blood Cancer Journal, 3, e159. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hishizawa, M. , Kanda, J. , Utsunomiya, A. , Taniguchi, S. , Eto, T. , Moriuchi, Y. , Tanosaki, R. , Kawano, F. , Miyazaki, Y. , Masuda, M. , Nagafuji, K. , Hara, M. , Takanashi, M. , Kai, S. , Atsuta, Y. , Suzuki, R. , Kawase, T. , Matsuo, K. , Nagamura‐Inoue, T. , Kato, S. , Sakamaki, H. , Morishima, Y. , Okamura, J. , Ichinohe, T. & Uchiyama, T. (2010) Transplantation of allogeneic hematopoietic stem cells for adult T‐cell leukemia: a nationwide retrospective study. Blood, 116, 1369–1376. - PubMed
-
- Ishida, T. & Ueda, R. (2011) Immunopathogenesis of lymphoma: focus on CCR4. Cancer Science, 102, 44–50. - PubMed
-
- Ishida, T. , Utsunomiya, A. , Iida, S. , Inagaki, H. , Takatsuka, Y. , Kusumoto, S. , Takeuchi, G. , Shimizu, S. , Ito, M. , Komatsu, H. , Wakita, A. , Eimoto, T. , Matsushima, K. & Ueda, R. (2003) Clinical significance of CCR4 expression in adult T‐cell leukemia/lymphoma: its close association with skin involvement and unfavorable outcome. Clinical Cancer Research, 9, 3625–3634. - PubMed
-
- Ishida, T. , Inagaki, H. , Utsunomiya, A. , Takatsuka, Y. , Komatsu, H. , Iida, S. , Takeuchi, G. , Eimoto, T. , Nakamura, S. & Ueda, R. (2004) CXC chemokine receptor 3 and CC chemokine receptor 4 expression in T‐cell and NK‐cell lymphomas with special reference to clinicopathological significance for peripheral T‐cell lymphoma, unspecified. Clinical Cancer Research, 10, 5494–5500. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

