Signaling pathways that control rho kinase activity maintain the embryonic epicardial progenitor state
- PMID: 25733666
- PMCID: PMC4400346
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M114.613190
Signaling pathways that control rho kinase activity maintain the embryonic epicardial progenitor state
Abstract
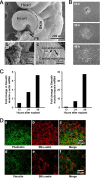
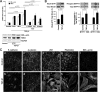
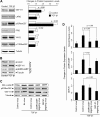
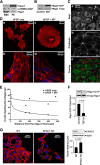
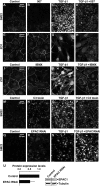
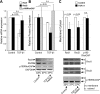
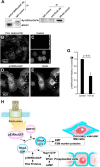
This study identifies signaling pathways that play key roles in the formation and maintenance of epicardial cells, a source of progenitors for coronary smooth muscle cells (SMCs). After epithelial to mesenchymal transition (EMT), mesenchymal cells invade the myocardium to form coronary SMCs. RhoA/Rho kinase activity is required for EMT and for differentiation into coronary SMCs, whereas cAMP activity is known to inhibit EMT in epithelial cells by an unknown mechanism. We use outgrowth of epicardial cells from E9.5 isolated mouse proepicardium (PE) explants, wild type and Epac1 null E12.5 mouse heart explants, adult rat epicardial cells, and immortalized mouse embryonic epicardial cells as model systems to identify signaling pathways that regulate RhoA activity to maintain the epicardial progenitor state. We demonstrate that RhoA activity is suppressed in the epicardial progenitor state, that the cAMP-dependent Rap1 GTP exchange factor (GEF), Epac, known to down-regulate RhoA activity through activation of Rap1 GTPase activity increased, that Rap1 activity increased, and that expression of the RhoA antagonistic Rnd proteins known to activate p190RhoGAP increased and associated with p190RhoGAP. Finally, EMT is associated with increased p63RhoGEF and RhoGEF-H1 protein expression, increased GEF-H1 activity, with a trend in increased p63RhoGEF activity. EMT is suppressed by partial silencing of p63RhoGEF and GEF-H1. In conclusion, we have identified new signaling molecules that act together to control RhoA activity and play critical roles in the maintenance of coronary smooth muscle progenitor cells in the embryonic epicardium. We suggest that their eventual manipulation could promote revascularization after myocardial injury.
Keywords: Cardiovascular; Epac; Epicardial Cells; Epithelial to Mesenchymal Transformation; Guanine Nucleotide Exchange Factor (GEF); Ras Homolog Gene Family, Member A (RhoA); Rnds; Signal Transduction; Transformation; p190RhoGAP.
© 2015 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Heparin inhibits pulmonary artery smooth muscle cell proliferation through guanine nucleotide exchange factor-H1/RhoA/Rho kinase/p27.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2011 Apr;44(4):524-30. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2010-0145OC. Epub 2010 Jun 17. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2011. PMID: 20558775 Free PMC article.
-
Claudin-2 suppresses GEF-H1, RHOA, and MRTF, thereby impacting proliferation and profibrotic phenotype of tubular cells.J Biol Chem. 2019 Oct 18;294(42):15446-15465. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA118.006484. Epub 2019 Sep 3. J Biol Chem. 2019. PMID: 31481470 Free PMC article.
-
The cAMP-responsive Rap1 guanine nucleotide exchange factor, Epac, induces smooth muscle relaxation by down-regulation of RhoA activity.J Biol Chem. 2011 May 13;286(19):16681-92. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.205062. Epub 2011 Mar 25. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21454546 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation and functions of the RhoA regulatory guanine nucleotide exchange factor GEF-H1.Small GTPases. 2021 Sep-Nov;12(5-6):358-371. doi: 10.1080/21541248.2020.1840889. Epub 2020 Oct 30. Small GTPases. 2021. PMID: 33126816 Free PMC article. Review.
-
p190RhoGAPs, the ARHGAP35- and ARHGAP5-Encoded Proteins, in Health and Disease.Cells. 2019 Apr 12;8(4):351. doi: 10.3390/cells8040351. Cells. 2019. PMID: 31013840 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Retinoic acid signaling promotes the cytoskeletal rearrangement of embryonic epicardial cells.FASEB J. 2018 Jul;32(7):3765-3781. doi: 10.1096/fj.201701038R. Epub 2018 Feb 15. FASEB J. 2018. PMID: 29447006 Free PMC article.
-
Semaphorin3F Drives Dendritic Spine Pruning Through Rho-GTPase Signaling.Mol Neurobiol. 2021 Aug;58(8):3817-3834. doi: 10.1007/s12035-021-02373-2. Epub 2021 Apr 15. Mol Neurobiol. 2021. PMID: 33856648 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of shRNA targeted against RhoA on proliferation and migration of human colonic cancer cells.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015 Jun 1;8(6):7040-4. eCollection 2015. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015. PMID: 26261596 Free PMC article.
-
Intracellular cAMP Sensor EPAC: Physiology, Pathophysiology, and Therapeutics Development.Physiol Rev. 2018 Apr 1;98(2):919-1053. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00025.2017. Physiol Rev. 2018. PMID: 29537337 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hic-5 regulates epithelial to mesenchymal transition in ovarian cancer cells in a TGFβ1-independent manner.Oncotarget. 2017 Jul 31;8(47):82506-82530. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.19714. eCollection 2017 Oct 10. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 29137281 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

