Effects of combined dietary supplementation with fenofibrate and Schisandrae Fructus pulp on lipid and glucose levels and liver function in normal and hypercholesterolemic mice
- PMID: 25733812
- PMCID: PMC4338776
- DOI: 10.2147/DDDT.S73544
Effects of combined dietary supplementation with fenofibrate and Schisandrae Fructus pulp on lipid and glucose levels and liver function in normal and hypercholesterolemic mice
Abstract
Background: Currently, combined therapy using herbs and synthetic drugs has become a feasible therapeutic intervention against some diseases. The purpose of this study was to assess the effects of supplementation with fenofibrate (FF), a chemical drug used for the treatment of hyperlipidemia, and the aqueous extract of Schisandrae Fructus (SF, a Chinese herb) pulp (AqSF-P) or an SF-related synthetic analog, bicyclol (BY), on serum/hepatic lipid levels and liver status in normal and hypercholesterolemic (HCL) mice.
Methods: Male mice obtained from the Institute of Cancer Research (ICR) were fed on a normal diet (ND) or high cholesterol/bile salt (0.5%/0.15%, w/w) diet (HCBD) containing FF (0.03% or 0.1%, w/w) with or without AqSF-P (0.3%-9.0%, based on crude herbal material, w/w) or BY (0.025%, w/w) for 10 days. Then serum lipid levels and alanine aminotransferase (ALT) activity, as well as hepatic triglyceride (TG), total cholesterol (TC), and glucose levels, were measured.
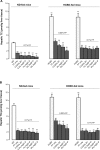
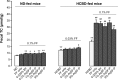
Results: Oral supplementation with FF significantly reduced serum and hepatic TG, TC, and hepatic glucose levels (approximately 79%) in mice fed with ND or HCBD. FF supplementation combined with AqSF-P or BY increased FF-induced reduction in hepatic TC and TG contents in ND-fed mice (up to 67%) and in HCBD-fed mice (up to 54%), when compared with FF supplementation alone. Hepatic glucose-lowering effect of FF was enhanced (up to 19%) by AqSF-P cosupplementation in both normal and HCL mice. FF supplementation enhanced the excretion of fecal TC (by 75%) in mice fed with HCBD. Fecal TC contents were increased by 14%/9% in the combination therapy with FF and AqSF-P in ND-/HCBD-fed mice. Serum ALT activity was elevated by 45% in HCBD-fed mice. FF caused a significant increase in ALT activity by 198% and 120% in normal and HCL mice, respectively. BY markedly attenuated the ALT activity by 54% in mice fed with ND supplemented with 0.1% FF and by 42% in mice fed with HCBD supplemented with 0.03% FF.
Conclusion: AqSF-P cosupplementation augmented the hepatic lipid-/glucose-lowering effects of FF. BY ameliorated FF-induced liver injury in normal and HCL mice.
Keywords: bicyclol; fat index; fatty liver disease; hepatotoxicity; interaction; synergist.
Figures


References
-
- Parikh NH, Parikh PK, Kothari C. Indigenous plant medicines for health care: treatment of diabetes mellitus and hyperlipidemia. Chin J Nat Med. 2014;12(5):335–344. - PubMed
-
- Bauer UE, Briss PA, Goodman RA, Bowman BA. Prevention of chronic disease in the 21st century: elimination of the leading preventable causes of premature death and disability in the USA. Lancet. 2014;384(9937):45–52. - PubMed
-
- Pan SY, Gao SH, Zhou SF, Tang MK, Yu ZL, Ko KM. New perspectives on complementary and alternative medicine: an overview and alternative therapy. Altern Ther Health Med. 2012;18(4):20–36. - PubMed
-
- Keating GM, Croom KF. Fenofibrate: a review of its use in primary dyslipidaemia, the metabolic syndrome and type 2 diabetes mellitus. Drugs. 2007;67(1):121–153. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

