Immunoglobulin isotypes in Atlantic salmon, Salmo salar
- PMID: 25734583
- PMCID: PMC4384117
- DOI: 10.3390/biom5010166
Immunoglobulin isotypes in Atlantic salmon, Salmo salar
Abstract
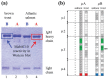
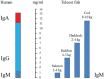
There are three major immunoglobulin (Ig) isotypes in salmonid fish: IgM, IgD and IgT, defined by the heavy chains μ, δ and τ, respectively. As a result of whole genome duplication in the ancestor of the salmonid fish family, Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) possess two highly similar Ig heavy chain gene complexes (A and B), comprising two μ genes, two δ genes, three intact τ genes and five τ pseudogenes. The μA and μB genes correspond to two distinct sub-populations of serum IgM. The IgM-B sub-variant has a characteristic extra cysteine near the C-terminal part of the heavy chain and exhibits a higher degree of polymer disulfide cross-linking compared to IgM-A. The IgM-B:IgM-A ratio in serum is typically 60:40, but skewed ratios are also observed. The IgT isotype appears to be specialized to mucosal immune responses in salmonid fish. The concentration of IgT in serum is 100 to 1000 times lower than IgM. Secreted forms of IgD have been detected in rainbow trout, but not yet in Atlantic salmon.
Figures

References
-
- Hikima J.-I., Jung T.-S., Aoki T. Immunoglobulin genes and their transcriptional control in teleosts. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2011;35:924–936. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

