Therapeutic advances in BIG3-PHB2 inhibition targeting the crosstalk between estrogen and growth factors in breast cancer
- PMID: 25736224
- PMCID: PMC4452155
- DOI: 10.1111/cas.12654
Therapeutic advances in BIG3-PHB2 inhibition targeting the crosstalk between estrogen and growth factors in breast cancer
Abstract
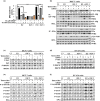
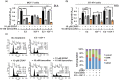
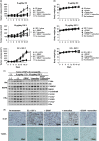
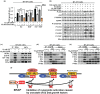
Our previous studies demonstrated that specific inhibition of the BIG3-PHB2 complex, which is a critical modulator in estrogen (E2) signaling, using ERAP, a dominant negative peptide inhibitor, leads to suppression of E2-dependent estrogen receptor (ER) alpha activation through the reactivation of the tumor suppressive activity of PHB2. Here, we report that ERAP has significant suppressive effects against synergistic activation caused by the crosstalk between E2 and growth factors associated with intrinsic or acquired resistance to anti-estrogen tamoxifen in breast cancer cells. Intrinsic PHB2 released from BIG3 by ERAP effectively disrupted each interaction of membrane-associated ERα and insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor beta (IGF-1Rβ), EGFR, PI3K or human epidermal growth factor 2 (HER2) in the presence of E2 and the growth factors IGF or EGF, followed by inhibited the activation of IGF-1Rβ, EGFR or HER2, and reduced Akt, MAPK and ERα phosphorylation levels, resulting in significant suppression of proliferation of ERα-positive breast cancer cells in vitro and in vivo. More importantly, combined treatment with ERAP and tamoxifen led to a synergistic suppression of signaling that was activated by crosstalk between E2 and growth factors or HER2 amplification. Taken together, our findings suggest that the specific inhibition of BIG3-PHB2 is a novel potential therapeutic approach for the treatment of tamoxifen-resistant breast cancers activated by the crosstalk between E2 and growth factor signaling, especially in premenopausal women.
Keywords: Crosstalk; PHB2; estrogen; growth factor; tamoxifen-resistance.
© 2015 The Authors. Cancer Science published by Wiley Publishing Asia Pty Ltd on behalf of Japanese Cancer Association.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Targeting BIG3-PHB2 interaction to overcome tamoxifen resistance in breast cancer cells.Nat Commun. 2013;4:2443. doi: 10.1038/ncomms3443. Nat Commun. 2013. PMID: 24051437 Free PMC article.
-
Stapled BIG3 helical peptide ERAP potentiates anti-tumour activity for breast cancer therapeutics.Sci Rep. 2017 May 12;7(1):1821. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-01951-6. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28500289 Free PMC article.
-
BIG3 Inhibits the Estrogen-Dependent Nuclear Translocation of PHB2 via Multiple Karyopherin-Alpha Proteins in Breast Cancer Cells.PLoS One. 2015 Jun 8;10(6):e0127707. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0127707. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26052702 Free PMC article.
-
Epidermal growth factor receptor/HER2/insulin-like growth factor receptor signalling and oestrogen receptor activity in clinical breast cancer.Endocr Relat Cancer. 2005 Jul;12 Suppl 1:S99-S111. doi: 10.1677/erc.1.01005. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2005. PMID: 16113104 Review.
-
Stemness Phenotype in Tamoxifen Resistant Breast Cancer Cells May be Induced by Interactions Between Receptor Tyrosine Kinases and ERα-66.Recent Pat Anticancer Drug Discov. 2018;13(3):302-307. doi: 10.2174/1574892813666180305164634. Recent Pat Anticancer Drug Discov. 2018. PMID: 29512469 Review.
Cited by
-
Minireview: The Link Between ERα Corepressors and Histone Deacetylases in Tamoxifen Resistance in Breast Cancer.Mol Endocrinol. 2016 Sep;30(9):965-76. doi: 10.1210/me.2016-1072. Epub 2016 Jul 20. Mol Endocrinol. 2016. PMID: 27581354 Free PMC article. Review.
-
C-Cbl reverses HER2-mediated tamoxifen resistance in human breast cancer cells.BMC Cancer. 2018 May 2;18(1):507. doi: 10.1186/s12885-018-4387-5. BMC Cancer. 2018. PMID: 29720121 Free PMC article.
-
Revisiting the IGF-1R as a breast cancer target.NPJ Precis Oncol. 2017;1:14. doi: 10.1038/s41698-017-0017-y. Epub 2017 May 1. NPJ Precis Oncol. 2017. PMID: 29152592 Free PMC article.
-
A-kinase anchoring protein BIG3 coordinates oestrogen signalling in breast cancer cells.Nat Commun. 2017 May 30;8:15427. doi: 10.1038/ncomms15427. Nat Commun. 2017. PMID: 28555617 Free PMC article.
-
Obesity Associated with Prediabetes Increases the Risk of Breast Cancer Development and Progression-A Study on an Obese Rat Model with Impaired Glucose Tolerance.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jul 14;24(14):11441. doi: 10.3390/ijms241411441. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37511200 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ali S, Coombes RC. Estrogen receptor a in human breast cancer: occurrence and significance. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 2000;5:271–81. - PubMed
-
- Kahlert S, Nuedling S, van Eickels M, Vetter H, Meyer R, Grohe C. Estrogen receptor α rapidly activates the IGF-1 receptor pathway. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:18447–53. - PubMed
-
- Pietras RJ. Interactions between estrogen and growth factor receptors in human breast cancers and the tumor-associated vasculature. Breast J. 2003;9:361–73. - PubMed
-
- Santen RJ, Song RX, Zhang Z, Yue W, Kumar R. Adaptive hypersensitivity to estrogen: mechanism for sequential responses to hormonal therapy in breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2004;10:337S–45S. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

