Astro-logics with microRNAs
- PMID: 25736376
- PMCID: PMC4426474
- DOI: 10.15252/embj.201591241
Astro-logics with microRNAs
Abstract
Astrocytes are a subtype of glial cells in the central nervous system that are critical for normal brain activity. In this issue of The EMBO Journal, Shenoy et al provide evidence for the involvement of miRNAs in the molecular mechanism underlying the in vitro differentiation of astrocytes from glial progenitor cells. Let-7 and miR-125 jointly silence multiple mRNA targets that would have potentially disrupted differentiation if expressed, and function in concert with JAK-STAT signaling to promote astrocyte differentiation.
Figures
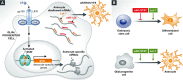
Comment on
-
Let-7 and miR-125 cooperate to prime progenitors for astrogliogenesis.EMBO J. 2015 May 5;34(9):1180-94. doi: 10.15252/embj.201489504. Epub 2015 Feb 23. EMBO J. 2015. PMID: 25715649 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bonni A, Sun Y, Nadal-Vicens M, Bhatt A, Frank DA, Rozovsky I, Stahl N, Yancopoulos GD, Greenberg ME. Regulation of gliogenesis in the central nervous system by the JAK-STAT signaling pathway. Science. 1997;278:477–483. - PubMed
-
- Giraldez AJ, Cinalli RM, Glasner ME, Enright AJ, Thomson JM, Baskerville S, Hammond SM, Bartel DP, Schier AF. MicroRNAs regulate brain morphogenesis in zebrafish. Science. 2005;308:833–838. - PubMed
-
- Hornstein E, Shomron N. Canalization of development by microRNAs. Nat Genet. 2006;38(Suppl):S20–S24. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

