Influence of dorsolateral prefrontal cortex and ventral striatum on risk avoidance in addiction: a mediation analysis
- PMID: 25736619
- PMCID: PMC4361089
- DOI: 10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2014.12.026
Influence of dorsolateral prefrontal cortex and ventral striatum on risk avoidance in addiction: a mediation analysis
Abstract
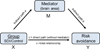
Background: Alterations in frontal and striatal function are hypothesized to underlie risky decision making in drug users, but how these regions interact to affect behavior is incompletely understood. We used mediation analysis to investigate how prefrontal cortex and ventral striatum together influence risk avoidance in abstinent drug users.
Method: Thirty-seven abstinent substance-dependent individuals (SDI) and 43 controls underwent fMRI while performing a decision-making task involving risk and reward. Analyses of a priori regions-of-interest tested whether activity in dorsolateral prefrontal cortex (DLPFC) and ventral striatum (VST) explained group differences in risk avoidance. Whole-brain analysis was conducted to identify brain regions influencing the negative VST-risk avoidance relationship.
Results: Right DLPFC (RDLPFC) positively mediated the group-risk avoidance relationship (p < 0.05); RDLPFC activity was higher in SDI and predicted higher risk avoidance across groups, controlling for SDI vs.
Controls: Conversely, VST activity negatively influenced risk avoidance (p < 0.05); it was higher in SDI, and predicted lower risk avoidance. Whole-brain analysis revealed that, across group, RDLPFC and left temporal-parietal junction positively (p ≤ 0.001) while right thalamus and left middle frontal gyrus negatively (p < 0.005) mediated the VST activity-risk avoidance relationship.
Conclusion: RDLPFC activity mediated less risky decision making while VST mediated more risky decision making across drug users and controls. These results suggest a dual pathway underlying decision making, which, if imbalanced, may adversely influence choices involving risk. Modeling contributions of multiple brain systems to behavior through mediation analysis could lead to a better understanding of mechanisms of behavior and suggest neuromodulatory treatments for addiction.
Keywords: Decision-making; Dorsolateral prefrontal cortex (DLPFC); Impulsivity; Mediation; Substance dependence; Ventral striatum (VST).
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Ireland Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no potential conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Baron RM, Kenny DA. The moderator-mediator variable distinction in social psychological research: conceptual, strategic, and statistical considerations. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 1986;51:1173–1182. - PubMed
-
- Bechara A, Damasio H. Decision-making and addiction (part I): impaired activation of somatic states in substance dependent individuals when pondering decisions with negative future consequences. Neuropsychologia. 2002;40:1675–1689. - PubMed
-
- Beck A, Schlagenhauf F, Wüstenberg T, Hein J, Kienast T, Kahnt T, Schmack K, Hägele C, Knutson B, Heinz A, Wrase J. Ventral striatal activation during reward anticipation correlates with impulsivity in alcoholics. Biol. Psychiatry. 2009;66:734–742. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

