PRMT9 is a type II methyltransferase that methylates the splicing factor SAP145
- PMID: 25737013
- PMCID: PMC4351962
- DOI: 10.1038/ncomms7428
PRMT9 is a type II methyltransferase that methylates the splicing factor SAP145
Abstract
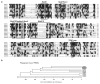
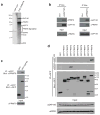
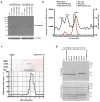
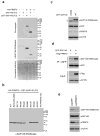
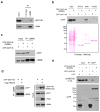
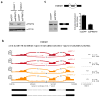
The human genome encodes a family of nine protein arginine methyltransferases (PRMT1-9), whose members can catalyse three distinct types of methylation on arginine residues. Here we identify two spliceosome-associated proteins-SAP145 and SAP49-as PRMT9-binding partners, linking PRMT9 to U2 snRNP maturation. We show that SAP145 is methylated by PRMT9 at arginine 508, which takes the form of monomethylated arginine (MMA) and symmetrically dimethylated arginine (SDMA). PRMT9 thus joins PRMT5 as the only mammalian enzymes capable of depositing the SDMA mark. Methylation of SAP145 on Arg 508 generates a binding site for the Tudor domain of the Survival of Motor Neuron (SMN) protein, and RNA-seq analysis reveals gross splicing changes when PRMT9 levels are attenuated. These results identify PRMT9 as a nonhistone methyltransferase that primes the U2 snRNP for interaction with SMN.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Gary JD, Clarke S. RNA and protein interactions modulated by protein arginine methylation. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1998;61:65–131. - PubMed
-
- Boffa LC, Karn J, Vidali G, Allfrey VG. Distribution of NG, NG,-dimethylarginine in nuclear protein fractions. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977;74:969–976. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

