Impaired Limb Proprioception in Adults With Spasmodic Dysphonia
- PMID: 25737471
- PMCID: PMC4551656
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jvoice.2014.12.010
Impaired Limb Proprioception in Adults With Spasmodic Dysphonia
Abstract
Objectives: Focal dystonia of the head and neck are associated with a loss of kinesthetic acuity at muscles distant from the dystonic sites. That is, while the motor deficits in focal dystonia are confined, the associated somatosensory deficits are generalized. This is the first systematic study to examine, if patients diagnosed with spasmodic dystonia (SD) show somatosensory impairments similar in scope to other forms of focal dystonia.
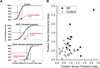
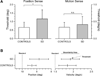
Methods: Proprioceptive acuity (ability to discriminate between two stimuli) for forearm position and motion sense was assessed in 14 spasmodic dystonia subjects and 28 age-matched controls using a passive motion apparatus. Psychophysical thresholds, uncertainty area (UA), and a proprioceptive acuity index (AI) were computed based on the subjects' verbal responses.
Results: The main findings are as follows: first, the SD group showed significantly elevated thresholds and UAs for forearm position sense compared with the control group. Second, 9 of 14 dystonia subjects (64%) exhibited an AI for position sense above the control group maximum. Three SD subjects had a motion sense AI above the control group maximum.
Conclusions: The results indicate that impaired limb proprioception is a common feature of SD. Like other forms of focal dystonia, spasmodic dystonia does affect the somatosensation of nondystonic muscle systems. That is, SD is associated with a generalized somatosensory deficit.
Keywords: Basal ganglia; Focal dystonia; Human; Kinesthesia; Somatosensation.
Copyright © 2015 The Voice Foundation. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Cohen LG, Ludlow C, Warden M, et al. Blink reflex excitability recovery curves in patients with spasmodic dysphonia. Neurology. 1989;39:572. - PubMed
-
- Tolosa E, Montserrat L. Depressed blink reflex habituation in dystonic blepharospasam. Neurology. 1985;35:251–260. - PubMed
-
- Tolosa E, Montserrat L, Bayes A. Blink reflex studies in focal dystonias: enhanced excitability of brainstem interneurons in cranial dystonia and spasmodic torticollis. Mov. Disord. 1988;3:61–69. - PubMed
-
- Topka H, Hallett M. Perioral reflexes in orofacial dyskinesia and spasmodic dysphonia. Muscle & Nerve. 1992;15:1016–1022. - PubMed
-
- Ludlow CL, Schulz GM, Yamashita T, Deleyiannis FW. Abnormalities in long latency responses to superior laryngeal nerve stimulation in adductor spasmodic dysphonia. Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. 1995;104:928–935. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

