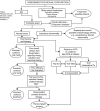
2015 CUA Practice guidelines for erectile dysfunction
- PMID: 25737750
- PMCID: PMC4336024
- DOI: 10.5489/cuaj.2699
2015 CUA Practice guidelines for erectile dysfunction
Figures
References
-
- Canadian Urological Guidelines Committee. Erectile dysfunction practice guidelines. Can J Urol. 2002;9:1583–87. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources