TLR7- and TLR9-responsive human B cells share phenotypic and genetic characteristics
- PMID: 25740945
- PMCID: PMC4369401
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.1402690
TLR7- and TLR9-responsive human B cells share phenotypic and genetic characteristics
Abstract
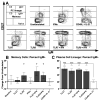
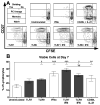
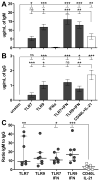
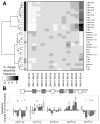
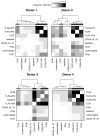
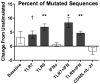
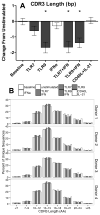
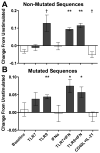
B cells activated by nucleic acid-sensing TLR7 and TLR9 proliferate and secrete immune globulins. Memory B cells are presumably more responsive due to higher TLR expression levels, but selectivity and differential outcomes remain largely unknown. In this study, peripheral blood human B cells were stimulated by TLR7 or TLR9 ligands, with or without IFN-α, and compared with activators CD40L plus IL-21, to identify differentially responsive cell populations, defined phenotypically and by BCR characteristics. Whereas all activators induced differentiation and Ab secretion, TLR stimulation expanded IgM(+) memory and plasma cell lineage committed populations, and favored secretion of IgM, unlike CD40L/IL-21, which drove IgM and IgG more evenly. Patterns of proliferation similarly differed, with CD40L/IL-21 inducing proliferation of most memory and naive B cells, in contrast with TLRs that induced robust proliferation in a subset of these cells. On deep sequencing of the IgH locus, TLR-responsive B cells shared patterns of IgHV and IgHJ usage, clustering apart from CD40L/IL-21 and control conditions. TLR activators, but not CD40L/IL-21, similarly promoted increased sharing of CDR3 sequences. TLR-responsive B cells were characterized by more somatic hypermutation, shorter CDR3 segments, and less negative charges. TLR activation also induced long positively charged CDR3 segments, suggestive of autoreactive Abs. Testing this, we found culture supernatants from TLR-stimulated B cells to bind HEp-2 cells, whereas those from CD40L/IL-21-stimulated cells did not. Human B cells possess selective sensitivity to TLR stimulation, with distinctive phenotypic and genetic signatures.
Copyright © 2015 by The American Association of Immunologists, Inc.
Figures
References
-
- Bekeredjian-Ding IB, Wagner M, Hornung V, Giese T, Schnurr M, Endres S, Hartmann G. Plasmacytoid dendritic cells control TLR7 sensitivity of naive B cells via type I IFN. J Immunol. 2005;174:4043–4050. - PubMed
-
- Glaum MC, Narula S, Song D, Zheng Y, Anderson AL, Pletcher CH, Levinson AI. Toll-like receptor 7-induced naive human B-cell differentiation and immunoglobulin production. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2009;123:224–230.e224. - PubMed
-
- He B, Qiao X, Cerutti A. CpG DNA induces IgG class switch DNA recombination by activating human B cells through an innate pathway that requires TLR9 and cooperates with IL-10. J Immunol. 2004;173:4479–4491. - PubMed
-
- Bernasconi NL, Onai N, Lanzavecchia A. A role for Toll-like receptors in acquired immunity: up-regulation of TLR9 by BCR triggering in naive B cells and constitutive expression in memory B cells. Blood. 2003;101:4500–4504. - PubMed
-
- Giordani L, Sanchez M, Libri I, Quaranta MG, Mattioli B, Viora M. IFN-alpha amplifies human naive B cell TLR-9-mediated activation and Ig production. J Leukoc Biol. 2009;86:261–271. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

