B cell Rab7 mediates induction of activation-induced cytidine deaminase expression and class-switching in T-dependent and T-independent antibody responses
- PMID: 25740947
- PMCID: PMC4643723
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.1401896
B cell Rab7 mediates induction of activation-induced cytidine deaminase expression and class-switching in T-dependent and T-independent antibody responses
Abstract
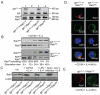
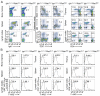
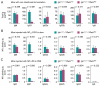
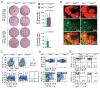
Class switch DNA recombination (CSR) is central to the maturation of the Ab response because it diversifies Ab effector functions. Like somatic hypermutation, CSR requires activation-induced cytidine deaminase (AID), whose expression is restricted to B cells, as induced by CD40 engagement or dual TLR-BCR engagement (primary CSR-inducing stimuli). By constructing conditional knockout Igh(+/C)γ(1-cre)Rab7(fl/fl) mice, we identified a B cell-intrinsic role for Rab7, a small GTPase involved in intracellular membrane functions, in mediating AID induction and CSR. Igh(+/C)γ(1-cre)Rab7(fl/fl) mice displayed normal B and T cell development and were deficient in Rab7 only in B cells undergoing Igh(C)γ(1-cre) Iγ1-Sγ1-Cγ1-cre transcription, as induced--like Igh germline Iγ1-Sγ1-Cγ1 and Iε-Sε-Cε transcription--by IL-4 in conjunction with a primary CSR-inducing stimulus. These mice could not mount T-independent or T-dependent class-switched IgG1 or IgE responses while maintaining normal IgM levels. Igh(+/C)γ(1-cre)Rab7(fl/fl) B cells showed, in vivo and in vitro, normal proliferation and survival, normal Blimp-1 expression and plasma cell differentiation, as well as intact activation of the noncanonical NF-κB, p38 kinase, and ERK1/2 kinase pathways. They, however, were defective in AID expression and CSR in vivo and in vitro, as induced by CD40 engagement or dual TLR1/2-, TLR4-, TLR7-, or TLR9-BCR engagement. In Igh(+/C)γ(1-cre)Rab7(fl/fl) B cells, CSR was rescued by enforced AID expression. These findings, together with our demonstration that Rab7-mediated canonical NF-κB activation, as critical to AID induction, outline a novel role of Rab7 in signaling pathways that lead to AID expression and CSR, likely by promoting assembly of signaling complexes along intracellular membranes.
Copyright © 2015 by The American Association of Immunologists, Inc.
Figures

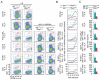
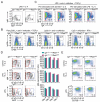


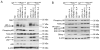
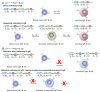
References
-
- Casali P. Somatic recombination and hypermutation in the immune system. In: Krebs JE, Goldstein ES, Kilpatrick ST, editors. Lewin's Genes XI. Jones & Bartlett; Sudbury, MA: 2014. pp. 459–507.
-
- Kato L, Stanlie A, Begum NA, Kobayashi M, Aida M, Honjo T. An evolutionary view of the mechanism for immune and genome diversity. J. Immunol. 2012;188:3559–3566. - PubMed
-
- Xu Z, Fulop Z, Wu G, Pone EJ, Zhang J, Mai T, Thomas LM, Al-Qahtani A, White CW, Park SR, Steinacker P, Li Z, Yates JRI, Herron B, Otto M, Zan H, Fu H, Casali P. 14-3-3 adaptor proteins recruit AID to 5′-AGCT-3′-rich switch regions for class switch recombination. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2010;17:1124–1135. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- AI 105813/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI079705/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- T32 AI 060573/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R56 AI079705/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI079705/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- GM 089919/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI105813/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R56 AI105813/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM089919/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI045011/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI130197/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AI129594/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AI124769/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

