Evaluation of patients' expectations and benefits in the treatment of allergic rhinitis with a new tool: the patient benefit index - the benefica study
- PMID: 25741366
- PMCID: PMC4349226
- DOI: 10.1186/s13223-015-0073-1
Evaluation of patients' expectations and benefits in the treatment of allergic rhinitis with a new tool: the patient benefit index - the benefica study
Abstract
Background: Symptoms of allergic rhinitis (AR) have a detrimental effect on quality of life. The AR-Patient Benefit Index (AR-PBI), a specific self-assessment tool has been developed to assess treatment-related benefit in two separate sections: the Patient Needs Questionnaire (PNQ) which explores the patient's expectations before treatment and the Patient Benefit Questionnaire (PBQ) which evaluates treatment benefit. For the PNQ, three dimensions summarize patients' expectations: symptoms, social life and emotional state, thus covering a larger field than symptomatic relief. The aim of the study was to validate the French language version of the AR-PBI and to assess the treatment-related expectations and benefits provided in patients with allergic rhinitis treated with H1-antihistamines in a real-life study.
Methods: BENEFICA was a prospective, observational study involving patients with allergic rhinitis who were starting treatment with H1-antihistamines. The Patient Needs Questionnaire (PNQ) was administered before treatment (D0) and the Patient Benefit Questionnaire (PBQ) was collected after a 14-day course of H1-antihistamines (D15). Discomfort (visual analog scale), and quality of life (miniRQLQ) were measured on D0 and D15.
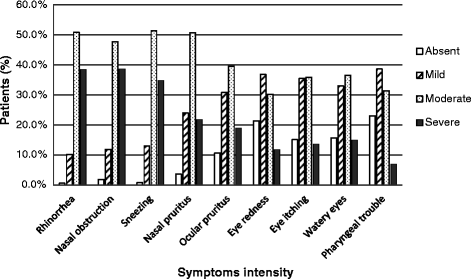
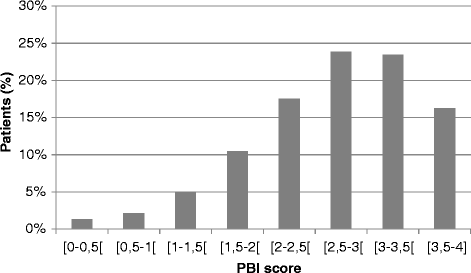
Results: Three thousands and eighty-nine patients were enrolled in the study: mean age 39 ± 14 years, women 52%, 81% of patients with moderate to severe persistent rhinitis (Allergic Rhinitis and its Impact on Asthma, ARIA); 19% had (a) concomitant condition(s), 18% were asthmatic, and 12% had atopic dermatitis. Discomfort and quality of life improved between D0 and D15. AR-PBI was 2.7 ± 0.8, superior to 1 (threshold for clinically relevant benefit) for 97% of patients and greater in patients willing to continue the treatment. PBI was moderately correlated to change in miniRQLQ (r = -0.45, p < 0.0001) and change in discomfort (r = -0.38, p < 0.0001), suggesting a richer conceptual content than symptoms relief.
Conclusions: The French version of the Allergic Rhinitis-Patient Benefit Index (AR-PBI) has been validated. It complements the discomfort and quality of life tools and assesses the needs and benefits in patients suffering from allergic rhinitis. This new tool may help physicians to better understand patients' expectations and to discuss treatment issues with their patients.
Keywords: AR-PBI; Allergic rhinitis; Antihistamine; Patient benefit index; Patients’ needs; Real-life study; Satisfaction; Treatment-related benefit.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Development and validation of a tool for the assessment of benefit from treatment of allergic rhinitis in children and adolescents (PBI-AR-K).Allergy Asthma Clin Immunol. 2022 Oct 25;18(1):95. doi: 10.1186/s13223-022-00733-8. Allergy Asthma Clin Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36284348 Free PMC article.
-
Allergic Rhinitis Control Test questionnaire-driven stepwise strategy to improve allergic rhinitis control: a prospective study.Allergy. 2016 Nov;71(11):1612-1619. doi: 10.1111/all.12963. Epub 2016 Jul 20. Allergy. 2016. PMID: 27332957
-
Validation of ARIA duration and severity classifications in Spanish allergic rhinitis patients - The ADRIAL cohort study.Rhinology. 2010 Jun;48(2):201-5. doi: 10.4193/Rhin09.099. Rhinology. 2010. PMID: 20502761
-
Desloratadine treatment for intermittent and persistent allergic rhinitis: a review.Clin Ther. 2007 Sep;29(9):1795-802. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2007.09.009. Clin Ther. 2007. PMID: 18035184 Review.
-
A treatment for allergic rhinitis: a view on the role of levocetirizine.Curr Med Res Opin. 2005 Jul;21(7):1099-106. doi: 10.1185/030079905X53298. Curr Med Res Opin. 2005. PMID: 16004679 Review.
Cited by
-
An observational cohort study of the use of five-grass-pollen extract sublingual immunotherapy during the 2015 pollen season in France.Allergy Asthma Clin Immunol. 2018 Sep 24;14:38. doi: 10.1186/s13223-018-0262-9. eCollection 2018. Allergy Asthma Clin Immunol. 2018. PMID: 30258465 Free PMC article.
-
Symptom importance, patient expectations, and satisfaction in chronic rhinosinusitis.Int Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2019 Jun;9(6):593-600. doi: 10.1002/alr.22309. Epub 2019 Feb 12. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2019. PMID: 30748101 Free PMC article.
-
Patient Needs and Treatment Goals in Chronic Atopic Pruritus: Does Eczema Make a Difference?Acta Derm Venereol. 2025 Mar 12;105:adv42773. doi: 10.2340/actadv.v105.42773. Acta Derm Venereol. 2025. PMID: 40077979 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

