Development of magnetic capture hybridization and quantitative polymerase chain reaction for hepatitis B virus covalently closed circular DNA
- PMID: 25741372
- PMCID: PMC4344652
- DOI: 10.5812/hepatmon.23729
Development of magnetic capture hybridization and quantitative polymerase chain reaction for hepatitis B virus covalently closed circular DNA
Abstract
Background: Hepatitis B virus (HBV) covalently closed circular DNA (cccDNA) served as a vital role in the life cycle of the virus and persistent infection. However, specific and quantitative methods for cccDNA detection have not been available.
Objectives: Our aim was to develop and primarily evaluate a quantitative method for HBV cccDNA based on magnetic capture hybridization and quantitative PCR technology.
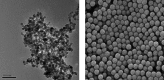
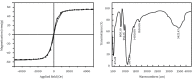
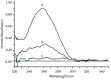
Materials and methods: The functionalized-nanoparticles specifically to capture HBV cccDNA, located on both sides of relaxed circle DNA (rcDNA) gap, were designed. Then, magnetic capture hybridization and quantitative PCR (MCH-qPCR) assay were developed and its performance was primarily evaluated with cccDNA standards and serum samples of patients with chronic hepatitis B.
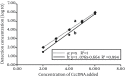
Results: Specific nanoparticles of cccDNA capture were prepared and a magnetic capture hybridization and quantitative assay method for cccDNA was developed successfully. The limit of detection was 90 IU/mL, and a good linear relationship in the range of 10(2)-10(6) IU/mL was revealed (r(2) = 0.994) with the MCH-qPCR. Compared with directly real-time PCR, a high content of HBV DNA did not affect the detection of cccDNA for the MCH-qPCR method, and there was no cross-reactivity between cccDNA and rcDNA.
Conclusions: The novel MCH-qPCR method has good sensitivity and specificity. It could meet the requirement of clinical routine detection.
Keywords: Hepatitis B Virus; Magnetic; PCR Technology.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Nested real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction assay for detection of hepatitis B virus covalently closed circular DNA.Chin Med J (Engl). 2011 May;124(10):1513-6. Chin Med J (Engl). 2011. PMID: 21740808
-
CRISPR/Cas13-assisted hepatitis B virus covalently closed circular DNA detection.Hepatol Int. 2022 Apr;16(2):306-315. doi: 10.1007/s12072-022-10311-0. Epub 2022 Mar 17. Hepatol Int. 2022. PMID: 35298777 Free PMC article.
-
[Comparative analysis of drug resistant mutations in the reverse transcriptase domain of hepatitis B virus covalently closed circular DNA and the viral relax circle DNA].Zhonghua Gan Zang Bing Za Zhi. 2010 Nov;18(11):818-21. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1007-3418.2010.11.007. Zhonghua Gan Zang Bing Za Zhi. 2010. PMID: 21138628 Chinese.
-
Persistence of hepatitis B virus covalently closed circular DNA in hepatocytes: molecular mechanisms and clinical significance.Emerg Microbes Infect. 2014 Sep;3(9):e64. doi: 10.1038/emi.2014.64. Epub 2014 Sep 17. Emerg Microbes Infect. 2014. PMID: 26038757 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Role for the Host DNA Damage Response in Hepatitis B Virus cccDNA Formation-and Beyond?Viruses. 2017 May 22;9(5):125. doi: 10.3390/v9050125. Viruses. 2017. PMID: 28531167 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Rapid and simultaneous detection of Salmonella spp., Escherichia coli O157, and Listeria monocytogenes by magnetic capture hybridization and multiplex real-time PCR.Folia Microbiol (Praha). 2018 Nov;63(6):735-742. doi: 10.1007/s12223-018-0617-0. Epub 2018 May 25. Folia Microbiol (Praha). 2018. PMID: 29797224
-
Simple and Reliable Method to Quantify the Hepatitis B Viral Load and Replicative Capacity in Liver Tissue and Blood Leukocytes.Hepat Mon. 2016 Feb 29;16(10):e28751. doi: 10.5812/hepatmon.28751. eCollection 2016 Oct. Hepat Mon. 2016. PMID: 27882060 Free PMC article.
-
Detection of hepatitis B virus infection: A systematic review.World J Hepatol. 2015 Oct 18;7(23):2482-91. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v7.i23.2482. World J Hepatol. 2015. PMID: 26483870 Free PMC article.
-
Role of hepatitis B virus in development of hepatocellular carcinoma: Focus on covalently closed circular DNA.World J Hepatol. 2022 May 27;14(5):866-884. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v14.i5.866. World J Hepatol. 2022. PMID: 35721287 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clinical Implications of Hepatitis B Virus RNA and Covalently Closed Circular DNA in Monitoring Patients with Chronic Hepatitis B Today with a Gaze into the Future: The Field Is Unprepared for a Sterilizing Cure.Genes (Basel). 2018 Oct 5;9(10):483. doi: 10.3390/genes9100483. Genes (Basel). 2018. PMID: 30301171 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Behnava B, Assari S, Amini M, Hajibeigi B, Jouybari HM, Alavian SM. HBV DNA viral load and chronic hepatitis infection in different stages. Hepat Mon. 2005;5(4):123–7.
-
- Mazet-Wagner AA, Baclet MC, Loustaud-Ratti V, Denis F, Alain S. Real-time PCR quantitation of hepatitis B virus total DNA and covalently closed circular DNA in peripheral blood mononuclear cells from hepatitis B virus-infected patients. J Virol Methods. 2006;138(1-2):70–9. doi: 10.1016/j.jviromet.2006.07.019. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Werle-Lapostolle B, Bowden S, Locarnini S, Wursthorn K, Petersen J, Lau G, et al. Persistence of cccDNA during the natural history of chronic hepatitis B and decline during adefovir dipivoxil therapy. Gastroenterology. 2004;126(7):1750–8. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
