An unusual abscess formation in the masticator space after acupressure massage: a case report
- PMID: 25741470
- PMCID: PMC4347032
- DOI: 10.5125/jkaoms.2015.41.1.52
An unusual abscess formation in the masticator space after acupressure massage: a case report
Abstract
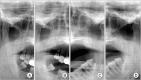
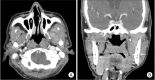
Clinical features of masticator-space abscess (MSA) are very similar to those of parotitis or temporomandibular disorder (TMD), making early differential diagnosis difficult. Local causes of MSA include nerve block anesthesia, infection after tooth extraction, and trauma to the temporomandibular joint (TMJ); the systemic cause is immunodeficiency. Odontogenic causes account for most etiologies, but there are also unusual causes of MSA. A 66-year-old male patient visited the emergency room (ER) presenting with left-side TMJ pain three days after receiving an acupressure massage. He was tentatively diagnosed with conventional post-trauma TMD and discharged with medication. However, the patient returned to the ER with increased pain. At this time, his TMD diagnosis was confirmed. He made a third visit to the ER during which facial computed tomographic (CT) images were taken. CT readings identified an abscess or hematoma in the left masticator space. After hospitalizing the patient, needle aspiration confirmed pus in the infratemporal and temporal fossa. Antibiotics were administered, and the abscess was drained through an incision made by the attending physician. The patient's symptoms decreased, and he was discharged.
Keywords: Abscess; Acupressure; Masticatory; Temporomandibular joint disorders.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures



References
-
- Curtin HD. Separation of the masticator space from the parapharyngeal space. Radiology. 1987;163:195–204. - PubMed
-
- Chong VF, Fan YF. Pictorial review: radiology of the masticator space. Clin Radiol. 1996;51:457–465. - PubMed
-
- Hasegawa T, Shibuya Y, Kuroki S, Takeuchi J, Yokoo S, Umeda M, et al. Two cases of masticator space abscess initially diagnosed as temporomandibular joint disorder. Kobe J Med Sci. 2008;54:E163–E168. - PubMed
-
- Kamath MP, Bhojwani KM, Mahale A, Meyyappan H, Abhijit K. Infratemporal fossa abscess: a diagnostic dilemma. Ear Nose Throat J. 2009;88:E23. - PubMed
-
- Raghava N, Evans K, Basu S. Infratemporal fossa abscess: complication of maxillary sinusitis. J Laryngol Otol. 2004;118:377–378. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

