Lincosamide synthetase--a unique condensation system combining elements of nonribosomal peptide synthetase and mycothiol metabolism
- PMID: 25741696
- PMCID: PMC4351081
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0118850
Lincosamide synthetase--a unique condensation system combining elements of nonribosomal peptide synthetase and mycothiol metabolism
Abstract
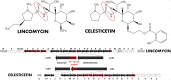
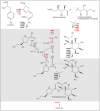
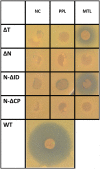
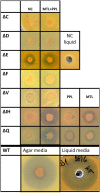
In the biosynthesis of lincosamide antibiotics lincomycin and celesticetin, the amino acid and amino sugar units are linked by an amide bond. The respective condensing enzyme lincosamide synthetase (LS) is expected to be an unusual system combining nonribosomal peptide synthetase (NRPS) components with so far unknown amino sugar related activities. The biosynthetic gene cluster of celesticetin was sequenced and compared to the lincomycin one revealing putative LS coding ORFs shared in both clusters. Based on a bioassay and production profiles of S. lincolnensis strains with individually deleted putative LS coding genes, the proteins LmbC, D, E, F and V were assigned to LS function. Moreover, the newly recognized N-terminal domain of LmbN (LmbN-CP) was also assigned to LS as a NRPS carrier protein (CP). Surprisingly, the homologous CP coding sequence in celesticetin cluster is part of ccbZ gene adjacent to ccbN, the counterpart of lmbN, suggesting the gene rearrangement, evident also from still active internal translation start in lmbN, and indicating the direction of lincosamide biosynthesis evolution. The in vitro test with LmbN-CP, LmbC and the newly identified S. lincolnensis phosphopantetheinyl transferase Slp, confirmed the cooperation of the previously characterized NRPS A-domain LmbC with a holo-LmbN-CP in activation of a 4-propyl-L-proline precursor of lincomycin. This result completed the functional characterization of LS subunits resembling NRPS initiation module. Two of the four remaining putative LS subunits, LmbE/CcbE and LmbV/CcbV, exhibit low but significant homology to enzymes from the metabolism of mycothiol, the NRPS-independent system processing the amino sugar and amino acid units. The functions of particular LS subunits as well as cooperation of both NRPS-based and NRPS-independent LS blocks are discussed. The described condensing enzyme represents a unique hybrid system with overall composition quite dissimilar to any other known enzyme system.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Peschke U, Schmidt H, Zhang HZ, Piepersberg W (1995) Molecular characterization of the lincomycin-production gene cluster of Streptomyces lincolnensis 78–11. Mol Microbiol 16: 1137–1156. - PubMed
-
- Piepersberg W (1995) Streptomycin and related aminoglycosides. Biotechnology (Reading, Mass) 28: 531–570. - PubMed
-
- Chung S- T, Manis JJ, McWethy SJ, Patt TE, Witz DF, Wolf HJ, et al. (1997) Fermentation, biosynthesis and molecular genetics of lincomycin In: Strohl WR, editor. Biotechnology of Antibiotics. 2 ed New York: Dekker; pp. 165–186.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

