Trabeculectomy-related complications in Olmsted County, Minnesota, 1985 through 2010
- PMID: 25742023
- PMCID: PMC4522324
- DOI: 10.1001/jamaophthalmol.2015.57
Trabeculectomy-related complications in Olmsted County, Minnesota, 1985 through 2010
Abstract
Importance: Trabeculectomy is the surgical standard of care for patients with medically refractory glaucoma. The use of antimetabolite agents, such as mitomycin, has increased the rate of complications after trabeculectomy.
Objective: To determine the rate of trabeculectomy-related complications during a 25-year study.
Design, setting, and participants: For this retrospective, population-based study, we enrolled the residents of Olmsted County, Minnesota, who underwent a trabeculectomy from January 1, 1985, through December 31, 2010, at the Mayo Clinic and Olmsted Community Hospital. Data were collected from August 2012 to September 2013 followed by data analysis through January 2014.
Exposures: After reviewing the patient records, we determined the occurrence of complications, including bleb leak, hypotony, hyphema, choroidal effusion, choroidal hemorrhage, blebitis, and endophthalmitis, as they relate to the mitomycin concentration administered during the operation. We reviewed relevant publications in Ovid, MEDLINE, and PubMed to identify studies representative of the reported trabeculectomy complication rate.
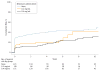
Main outcomes and measures: Cumulative probabilities of short- and long-term complications, determined using the Kaplan-Meier method, and the relation to mitomycin concentration applied during trabeculectomy.
Results: In 334 patients, 460 eyes underwent trabeculectomy (mean [SD; range] follow-up, 7.7 [5.7; 0-27.7] years). Among them, 159 eyes had complications, with early complications (<3 months) in 100 eyes and late complications (≥3 months) in 59 eyes during the follow-up. Ten eyes had an early and a late complication. The 20-year cumulative chances of early, late, or any complication were 19.7% (95% CI, 16.2%-23.6%), 26.0% (95% CI, 15.0%-36.0%), and 45.0% (95% CI, 38.0%-52.0%), respectively. The cumulative probabilities of vision-threatening complications during 20 years were 2.0% (95% CI, 0%-4.0%) for blebitis and 5.0% (95% CI, 1.0%-9.0%) for endophthalmitis. Association between the rate of trabeculectomy complications and mitomycin dose used was P = .77. In total, 98 cases (21.3%) underwent further surgical procedures related directly to the complication.
Conclusions and relevance: The rate of trabeculectomy-related complications does not appear to be associated with mitomycin use during a mean follow-up of 7.7 years. The rate of vision-threatening complications appears to be comparable to those of previous studies of shorter duration.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Long-Term Outcomes of Trabeculectomy Augmented with Mitomycin C Undertaken within the First 2 Years of Life.Ophthalmology. 2015 Nov;122(11):2216-22. doi: 10.1016/j.ophtha.2015.07.028. Epub 2015 Aug 24. Ophthalmology. 2015. PMID: 26315044
-
Surgical results and complications of mitomycin C-augmented trabeculectomy in refractory developmental glaucoma.Ophthalmic Surg Lasers. 1999 Jun;30(6):473-80. Ophthalmic Surg Lasers. 1999. PMID: 10392736
-
Incidence of late-onset bleb-related complications following trabeculectomy with mitomycin.Arch Ophthalmol. 2002 Mar;120(3):297-300. doi: 10.1001/archopht.120.3.297. Arch Ophthalmol. 2002. PMID: 11879132
-
Bleb-related infection after primary trabeculectomy: medical chart reviews from 1993 to 2021.Br J Ophthalmol. 2023 Dec 18;108(1):58-64. doi: 10.1136/bjo-2022-321429. Br J Ophthalmol. 2023. PMID: 36283798 Review.
-
Choroidal effusions after glaucoma surgery.Curr Opin Ophthalmol. 2015 Mar;26(2):134-42. doi: 10.1097/ICU.0000000000000131. Curr Opin Ophthalmol. 2015. PMID: 25643198 Review.
Cited by
-
Real-world evaluation of novel eye drop bottle sensors: Cloud-based AI support for eye drop adherence.Heliyon. 2024 Jul 5;10(14):e34167. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e34167. eCollection 2024 Jul 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39092249 Free PMC article.
-
EX-PRESS Glaucoma Filtration Device: Management of Complications.Vision (Basel). 2020 Aug 16;4(3):39. doi: 10.3390/vision4030039. Vision (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32824320 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A novel use of the endoscopic cyclophotocoagulative probe for the management of excisional goniotomy induced chronic recurrent hyphema.Am J Ophthalmol Case Rep. 2022 Mar 17;26:101492. doi: 10.1016/j.ajoc.2022.101492. eCollection 2022 Jun. Am J Ophthalmol Case Rep. 2022. PMID: 35340745 Free PMC article.
-
Retinal Pigment Epithelial Tears after Ex-PRESS Filtration Surgery in a Glaucoma Patient with a History of Ischemic Optic Neuropathy.Case Rep Ophthalmol Med. 2023 Oct 25;2023:6645156. doi: 10.1155/2023/6645156. eCollection 2023. Case Rep Ophthalmol Med. 2023. PMID: 37920746 Free PMC article.
-
Scleral concave pool trabeculectomy combined phacoemulsification in primary open-angle glaucoma with cataract.BMC Ophthalmol. 2020 Jun 9;20(1):222. doi: 10.1186/s12886-020-01500-2. BMC Ophthalmol. 2020. PMID: 32517766 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Higginbotham EJ, Stevens RK, Musch DC, et al. Bleb-related endophthalmitis after trabeculectomy with mitomycin C. Ophthalmology. 1996;103(4):650–656. - PubMed
-
- Lama PJ, Fechtner RD. Antifibrotics and wound healing in glaucoma surgery. Surv Ophthalmol. 2003;48(3):314–346. - PubMed
-
- Palmer SS. Mitomycin as adjunct chemotherapy with trabeculectomy. Ophthalmology. 1991;98(3):317–321. - PubMed
-
- Parc CE, Johnson DH, Oliver JE, Hattenhauer MG, Hodge DO. The long-term outcome of glaucoma filtration surgery. Am J Ophthalmol. 2001;132(1):27–35. - PubMed
-
- Reibaldi A, Uva MG, Longo A. Nine-year follow-up of trabeculectomy with or without low-dosage mitomycin-C in primary open-angle glaucoma. Br J Ophthalmol. 2008;92(12):1666–1670. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

