Correlation of extended RAS and PIK3CA gene mutation status with outcomes from the phase III AGITG MAX STUDY involving capecitabine alone or in combination with bevacizumab plus or minus mitomycin C in advanced colorectal cancer
- PMID: 25742472
- PMCID: PMC4366893
- DOI: 10.1038/bjc.2015.37
Correlation of extended RAS and PIK3CA gene mutation status with outcomes from the phase III AGITG MAX STUDY involving capecitabine alone or in combination with bevacizumab plus or minus mitomycin C in advanced colorectal cancer
Abstract
Background: Mutations affecting RAS genes are now established predictive markers of nonresponse to anti-EGFR antibodies in advanced CRC. This analysis assessed the prognostic and predictive impact of extended RAS and PIK3CA gene mutation status in patients receiving capecitabine plus or minus bevacizumab (±mitomycin C) in the randomised phase III MAX study.
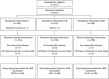
Methods: DNA was extracted from archival macrodissected formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded tumour tissue. Mutation status was determined using pyrosequencing, confirmed with Sanger sequencing (for equivocal RAS) and correlated with efficacy outcomes. Predictive analyses were undertaken using a test for interaction involving both C vs CB+CBM.
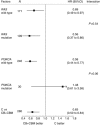
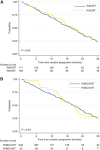
Results: Of the available 280 of the 471 (59.4%) patients, mutations in KRAS exons 2, 3 and 4 and NRAS 2, 3 and 4 were as follows: 32%, 2.9%, 2.2%, 1.4%, 0.7% and 0% (total RAS MT 39%). The PIK3CA MT rate was 7.5% exon 9 and 3.6% exon 20. Extended RAS gene mutation status (WT vs MT) had no prognostic impact for PFS (HR 0.91 (0.71-1.17)) or OS (HR 0.95 (0.71-1.25)). The RAS gene mutation status was not predictive of the effectiveness of bevacizumab for PFS (HR 0.56 (0.37-0.85) for RAS MT and HR 0.69 (0.5-0.97) for RAS WT; P for interaction 0.50). The PIK3CA mutation was neither predictive for bevacizumab effect nor prognostic.
Conclusion: Of KRAS exon 2 WT patients, 10% had additional RAS mutations. Neither all RAS gene mutation status nor PIK3CA mutation status was prognostic for PFS or OS, or predictive of bevacizumab outcome in patients with advanced CRC.
Figures
References
-
- Amado RG, Wolf M, Peeters M, Van Cutsem E, Siena S, Freeman DJ, Juan T, Sikorski R, Suggs S, Radinsky R, Patterson SD, Chang DD. Wild-type KRAS is required for panitumumab efficacy in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2008;26 (10:1626–1634. - PubMed
-
- Bokemeyer C, Bondarenko I, Hartmann JT, de Braud F, Schuch G, Zubel A, Celik I, Schlichting M, Koralewski P. Efficacy according to biomarker status of cetuximab plus FOLFOX-4 as first-line treatment for metastatic colorectal cancer: the OPUS study. Ann Oncol. 2011;22 (7:1535–1546. - PubMed
-
- Bokemeyer C, Kohne C-H, Ciardiello F, Lenz H-J, Heinemann V, Klinkhardt U, Beier F, Duecker K, Tejpar S. Treatment outcome according to tumor RAS mutation status in OPUS study patients with metastatic colorectal cancer (mCRC) randomized to FOLFOX4 with/without cetuximab. J Clin Oncol. 2014;32 (Suppl 5:abstr 3505.
-
- Ciardiello F, Lenz H-J, Kohne C-H, Heinemann V, Tejpar S, Melezinek I, Beier F, Stroh C, Van Cutsem E. Treatment outcome according to tumor RAS mutation status in CRYSTAL study patients with metastatic colorectal cancer (mCRC) randomized to FOLFIRI with/without cetuximab. J Clin Oncol. 2014;32 (Suppl 5:abstr 3506.
-
- Ciardiello F, Troiani T, Bianco R, Orditura M, Morgillo F, Martinelli E, Morelli MP, Cascone T, Tortora G. Interaction between the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) and the vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) pathways: a rational approach for multi-target anticancer therapy. Ann Oncol. 2006;17 (Suppl 7:vii109–vii114. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

