Induction of cellular prion protein (PrPc) under hypoxia inhibits apoptosis caused by TRAIL treatment
- PMID: 25742790
- PMCID: PMC4467153
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.3028
Induction of cellular prion protein (PrPc) under hypoxia inhibits apoptosis caused by TRAIL treatment
Abstract
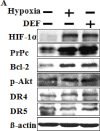
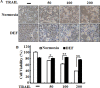
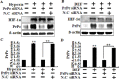
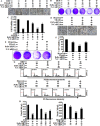
Hypoxia decreases cytotoxic responses to tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) protein. Cellular prion protein (PrPc) is regulated by HIF-1α in neurons. We hypothesized that PrPc is involved in hypoxia-mediated resistance to TRAIL-induced apoptosis. We found that hypoxia induced PrPc protein and inhibited TRAIL-induced apoptosis. Thus silencing of PrPc increased TRAIL-induced apoptosis under hypoxia. Overexpression of PrPc protein using an adenoviral vector inhibited TRAIL-induced apoptosis. In xenograft model in vivo, shPrPc transfected cells were more sensitive to TRAIL-induced apoptosis than in shMock transfected cells. Molecular chemo-therapy approaches based on the regulation of PrPc expression need to address anti-tumor function of TRAIL under hypoxia. Molecular chemo-therapy approaches based on the regulation of PrPc expression need to address anti-tumor function of TRAIL under hypoxia.
Keywords: HIF-1α; PrPc; TRAIL; colon cancer; hypoxia.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

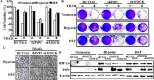

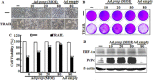
Similar articles
-
MiR-338-3p inhibits hepatocarcinoma cells and sensitizes these cells to sorafenib by targeting hypoxia-induced factor 1α.PLoS One. 2014 Dec 22;9(12):e115565. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0115565. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25531114 Free PMC article.
-
Oncolytic reovirus combined with trastuzumab enhances antitumor efficacy through TRAIL signaling in human HER2-positive gastric cancer cells.Cancer Lett. 2015 Jan 28;356(2 Pt B):846-54. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2014.10.046. Epub 2014 Nov 17. Cancer Lett. 2015. PMID: 25444894
-
Hypoxia-inducible factor-1 α regulates prion protein expression to protect against neuron cell damage.Neurobiol Aging. 2012 May;33(5):1006.e1-10. doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2011.09.037. Epub 2011 Oct 28. Neurobiol Aging. 2012. PMID: 22036844
-
Hypoxia inducing factor-1alpha regulates tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand sensitivity in tumor cells exposed to hypoxia.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2010 Aug 27;399(3):379-83. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2010.07.082. Epub 2010 Jul 24. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2010. PMID: 20659427
-
The normal cellular prion protein and its possible role in angiogenesis.Front Biosci. 2008 May 1;13:6491-500. doi: 10.2741/3169. Front Biosci. 2008. PMID: 18508675 Review.
Cited by
-
High cellular prion protein expression in cholangiocarcinoma: A marker for early postoperative recurrence and unfavorable prognosis.World J Gastrointest Surg. 2025 Mar 27;17(3):101940. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v17.i3.101940. World J Gastrointest Surg. 2025. PMID: 40162420 Free PMC article.
-
Cellular Prion Protein (PrPc) and Hypoxia: True to Each Other in Good Times and in Bad, in Sickness, and in Health.Front Cell Neurosci. 2016 Dec 19;10:292. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2016.00292. eCollection 2016. Front Cell Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 28066187 Free PMC article.
-
Wnt, glucocorticoid and cellular prion protein cooperate to drive a mesenchymal phenotype with poor prognosis in colon cancer.J Transl Med. 2024 Apr 8;22(1):337. doi: 10.1186/s12967-024-05164-0. J Transl Med. 2024. PMID: 38589873 Free PMC article.
-
Hypoxia regulates TRAIL sensitivity of colorectal cancer cells through mitochondrial autophagy.Oncotarget. 2016 Jul 5;7(27):41488-41504. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.9206. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27166192 Free PMC article.
-
The Cellular Prion Protein and the Hallmarks of Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Oct 8;13(19):5032. doi: 10.3390/cancers13195032. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34638517 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Srivastava RK. Intracellular mechanisms of TRAIL and its role in cancer therapy. Mol Cell Biol Res Commun. 2000;4:67–75. - PubMed
-
- Almasan A, Ashkenazi A. Apo2L/TRAIL: apoptosis signaling, biology, and potential for cancer therapy. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2003;14:337–348. - PubMed
-
- Chen X, Thakkar H, Tyan F, Gim S, Robinson H, Lee C, Pandey SK, Nwokorie C, Onwudiwe N, Srivastava RK. Constitutively active Akt is an important regulator of TRAIL sensitivity in prostate cancer. Oncogene. 2001;20:6073–6083. - PubMed
-
- Singh TR, Shankar S, Chen X, Asim M, Srivastava RK. Synergistic interactions of chemotherapeutic drugs and tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand/Apo-2 ligand on apoptosis and on regression of breast carcinoma in vivo. Cancer research. 2003;63:5390–5400. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

