Computational design, chemical synthesis, and biological evaluation of a novel ERK inhibitor (BL-EI001) with apoptosis-inducing mechanisms in breast cancer
- PMID: 25742792
- PMCID: PMC4466648
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.3105
Computational design, chemical synthesis, and biological evaluation of a novel ERK inhibitor (BL-EI001) with apoptosis-inducing mechanisms in breast cancer
Abstract
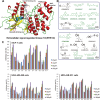
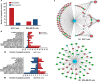
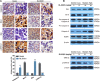
Extracellular signal-regulated kinase1/2 (ERK1/2) plays a crucial role in the resistance of apoptosis in carcinogenesis; however, its targeted small-molecule inhibitors still remain to be discovered. Thus, in this study, we computationally and experimentally screened a series of small-molecule inhibitors targeting ERK toward different types of human breast cancer cells. Subsequently, we synthesized some candidate ERK inhibitors, identified a novel ERK inhibitor (BL-EI001) with anti-proliferative activities, and analyzed the BL-EI001/ERK complex. Moreover, we found that BL-EI001 induced breast cancer cell apoptosis via mitochondrial pathway but independent on Ras/Raf/MEK pathway. In addition, we carried out proteomics analyses for exploring some possible BL-EI001-induced apoptotic pathways, and further found that BL-EI001-induced apoptosis affected ERK phosphorylation in breast cancer. Further, we found that BL-EI001 bear anti-tumor activities without remarkable toxicities, and also induced mitochondrial apoptosis by targeting ERK in vivo. Taken together, these results demonstrate that in silico design and experimental discovery of a synthesized small-molecule ERK inhibitor (BL-EI001)as a potential novel apoptosis-inducing drug in the treatment of breast cancer.
Keywords: ERK inhibitor (BL-EI001); apoptosis; breast cancer; extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 (ERK1/2); mitochondrial pathway.
Conflict of interest statement
None of the authors have a financial interest to declare.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Integrated bioinformatics, computational and experimental methods to discover novel Raf/extracellular-signal regulated kinase (ERK) dual inhibitors against breast cancer cells.Eur J Med Chem. 2017 Feb 15;127:997-1011. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2016.11.009. Epub 2016 Nov 8. Eur J Med Chem. 2017. PMID: 27839788
-
Role of RAF/MEK/ERK pathway, p-STAT-3 and Mcl-1 in sorafenib activity in human pancreatic cancer cell lines.J Cell Physiol. 2009 Jul;220(1):214-21. doi: 10.1002/jcp.21753. J Cell Physiol. 2009. PMID: 19288493
-
Repositioning of amprenavir as a novel extracellular signal-regulated kinase-2 inhibitor and apoptosis inducer in MCF-7 human breast cancer.Int J Oncol. 2017 Mar;50(3):823-834. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2017.3860. Epub 2017 Jan 24. Int J Oncol. 2017. PMID: 28197631
-
Molecular Targeting of ERKs/RSK2 Signaling in Cancers.Curr Pharm Des. 2017 Nov 16;23(29):4247-4258. doi: 10.2174/1381612823666170714142338. Curr Pharm Des. 2017. PMID: 28714417 Review.
-
Targeting the extracellular signal-regulated kinase pathway in cancer therapy.Biol Pharm Bull. 2011;34(12):1781-4. doi: 10.1248/bpb.34.1781. Biol Pharm Bull. 2011. PMID: 22130230 Review.
Cited by
-
Small Molecule Therapeutics in the Pipeline Targeting for Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: Origin, Challenges, Opportunities, and Mechanisms of Action.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jun 6;25(11):6285. doi: 10.3390/ijms25116285. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38892472 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Long non-coding RNA NEAT1 regulates epithelial membrane protein 2 expression to repress nasopharyngeal carcinoma migration and irradiation-resistance through miR-101-3p as a competing endogenous RNA mechanism.Oncotarget. 2017 Jul 26;8(41):70156-70171. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.19596. eCollection 2017 Sep 19. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 29050268 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of HSP90 sensitizes a novel Raf/ERK dual inhibitor CY-9d in triple-negative breast cancer cells.Oncotarget. 2017 Oct 26;8(61):104193-104205. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.22119. eCollection 2017 Nov 28. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 29262632 Free PMC article.
-
Macrophage polarization and acceleration of atherosclerotic plaques in a swine model.PLoS One. 2018 Mar 21;13(3):e0193005. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0193005. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 29561847 Free PMC article.
-
Synergistic inhibition of MEK and reciprocal feedback networks for targeted intervention in malignancy.Cancer Biol Med. 2019 Aug;16(3):415-434. doi: 10.20892/j.issn.2095-3941.2019.0137. Cancer Biol Med. 2019. PMID: 31565475 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dhillon AS, Hagan S, Rath O, Kolch W. MAP kinase signaling pathways in cancer. Oncogene. 2007;26:3279–3290. - PubMed
-
- Kim EK, Choi EJ. Pathological roles of MAPK signaling pathways in human diseases. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2010;1802:396–405. - PubMed
-
- Lu Z, Xu S. ERK1/2 MAP kinases in cell survival and apoptosis. IUBMB. Life. 2006;58:621–631. - PubMed
-
- Roskoski R., Jr ERK1/2 MAP kinases: Structure, function, and regulation. Pharmacol Res. 2012;66:105–143. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

