Does Measurement of Esophagogastric Junction Distensibility by EndoFLIP Predict Therapy- responsiveness to Endoluminal Fundoplication in Patients With Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease?
- PMID: 25742904
- PMCID: PMC4398245
- DOI: 10.5056/jnm14111
Does Measurement of Esophagogastric Junction Distensibility by EndoFLIP Predict Therapy- responsiveness to Endoluminal Fundoplication in Patients With Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease?
Abstract
Background/aims: In patients with gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), an increased esophagogastric junction (EGJ) distensibility has been described. Assessment of EGJ distensibility with the endoscopic functional luminal imaging probe (EndoFLIP) technique might identify patients responsive to transoral incisionless fundoplication (TIF), whereas postoperative measurement of EGJ distensibility might provide insight into the antireflux mechanism of TIF. Therefore, we investigated the value of the EndoFLIP technique in GERD patients treated by TIF.
Methods: Forty-two GERD patients underwent EGJ distensibility measurement before TIF using the EndoFLIP technique. In a subgroup of 25 patients, EndoFLIP measurement was repeated both postoperative and at 6 months follow-up. Treatment outcome was assessed according to esophageal acid exposure time (AET; objective outcome) and symptom scores (clinical outcome) 6 months after TIF.
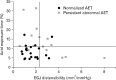
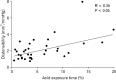
Results: Multiple logistic regression analysis showed that preoperative EGJ distensibility (OR, 0.16; 95% CI, 0.03-0.78; P = 0.023) and preoperative AET (OR, 0.62; 95% CI, 0.42-0.90; P = 0.013) were independent predictors for objective treatment outcome but not for clinical outcome after TIF. The best cut-off value for objective outcome was 2.3 mm(2)/mmHg for preoperative EGJ distensibility and 11% for preoperative AET. EGJ distensibility decreased direct postoperative from 2.0 (1.2-3.3) to 1.4 (1.0-2.2) mm(2)/mmHg (P = 0.014), but increased to 2.2 (1.5-3.0) at 6 months follow-up (P = 0.925, compared to preoperative).
Conclusions: Preoperative EGJ distensibility and preoperative AET were independent predictors for objective treatment outcome but not for clinical outcome after TIF. According to our data, the EndoFLIP technique has no added value either in the preoperative diagnostic work-up or in the post-procedure evaluation of endoluminal antireflux therapy.
Keywords: Esophagogastric Junction; Fundoplication; Gastroesophageal reflux disease; Treatment outcome.
Figures

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

