Functional interaction of nicotinic acetylcholine receptors and Na+/K+ ATPase from Locusta migratoria manilensis (Meyen)
- PMID: 25743085
- PMCID: PMC4351541
- DOI: 10.1038/srep08849
Functional interaction of nicotinic acetylcholine receptors and Na+/K+ ATPase from Locusta migratoria manilensis (Meyen)
Abstract
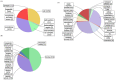
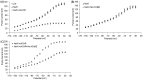
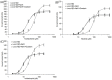
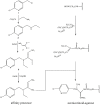
Associated proteins are important for the correct functioning of nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (nAChRs). In the present study, a neonicotinoid-agarose affinity column was used to isolate related proteins from a solubilized membrane preparation from the nervous system of Locusta migratoria manilensis (Meyen). 1530 peptides were identified and most of them were involved in the membranous structure, molecular interaction and cellular communication. Among these peptides, Na(+)/K(+) ATPase had the highest MASCOT score and were involved in the molecular interaction, which suggested that Na(+)/K(+) ATPase and nAChRs might have strong and stable interactions in insect central nervous system. In the present study, functional interactions between nAChRs and Na(+)/K(+) ATPase were examined by heterologous expression in Xenopus oocytes. The results showed that the activated nAChRs increased pump currents of Na(+)/K(+) ATPase, which did not require current flow through open nAChRs. In turn, Na(+)/K(+) ATPase significantly increased agonist sensitivities of nAChRs in a pump activity-independent manner and reduced the maximum current (Imax) of nAChRs. These findings provide novel insights concerning the functional interactions between insect nAChRs and Na(+)/K(+) ATPase.
Figures


References
-
- Sattelle D. B. & Breer H. Cholinergic nerve-terminals in the central-nervous-system of insects - molecular aspects of structure, function and regulation. J. Neuroendocrinol. 2, 241–256 (1990). - PubMed
-
- Matsuda K. et al. Neonicotinoids: Insecticides acting on insect nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 22, 573–580 (2001). - PubMed
-
- Geng C., Watson G. B. & Sparks T. C. Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors as Spinosyn Targets for Insect Pest Management Target Receptors in The Control of Insect Pests: Part I. Cohen E. (ed.) 101–210 (Academic Press, London, 2013).
-
- Sattelle D. B. et al. Nereistoxin - actions on a CNS acetylcholine-receptor ion channel in the cockroach Periplaneta americana. J. Exp. Biol. 118, 37–52 (1985).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

