Vaginal Cytomegalovirus Shedding Before and After Initiation of Antiretroviral Therapy in Rakai, Uganda
- PMID: 25743428
- PMCID: PMC4548459
- DOI: 10.1093/infdis/jiv135
Vaginal Cytomegalovirus Shedding Before and After Initiation of Antiretroviral Therapy in Rakai, Uganda
Abstract
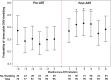
Vaginal shedding of cytomegalovirus (CMV) DNA was determined longitudinally among 96 women coinfected with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), herpes simplex virus 2, and CMV starting antiretroviral therapy (ART) during a placebo-controlled trial of HSV-2 suppression with acyclovir in Rakai, Uganda. Vaginal CMV was detected in 75 of 96 women (78.0%) and 379 of 1080 individual visits (35.1%). ART status, higher HIV RNA viral load before ART initiation, and younger age were significantly associated with increased frequency of CMV shedding (P < .01). Compared to pre-ART, CMV shedding peaked from month 2 to month 4 after ART initiation, suggesting possible immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome. Further studies need to determine the clinical significance of asymptomatic CMV shedding.
Keywords: Uganda; acyclovir; antiretroviral therapy (ART); cytomegalovirus (CMV); human immunodeficiency virus (HIV); immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome (IRIS); reactivation.
© The Author 2015. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Infectious Diseases Society of America. All rights reserved. For Permissions, please e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Reactivation of herpes simplex virus type 2 after initiation of antiretroviral therapy.J Infect Dis. 2013 Sep 1;208(5):839-46. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jit252. Epub 2013 Jun 28. J Infect Dis. 2013. PMID: 23812240 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Subclinical Genital Herpes Shedding in HIV/Herpes Simplex Virus 2-Coinfected Women during Antiretroviral Therapy Is Associated with an Increase in HIV Tissue Reservoirs and Potentially Promotes HIV Evolution.J Virol. 2020 Dec 9;95(1):e01606-20. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01606-20. Print 2020 Dec 9. J Virol. 2020. PMID: 33028713 Free PMC article.
-
Transient Increase in Herpes Simplex Virus Type 2 (HSV-2)-Associated Genital Ulcers Following Initiation of Antiretroviral Therapy in HIV/HSV-2-Coinfected Individuals.J Infect Dis. 2016 May 15;213(10):1573-8. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiv765. Epub 2015 Dec 23. J Infect Dis. 2016. PMID: 26704611 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Valaciclovir: a review of its long term utility in the management of genital herpes simplex virus and cytomegalovirus infections.Drugs. 2000 Apr;59(4):839-63. doi: 10.2165/00003495-200059040-00013. Drugs. 2000. PMID: 10804039 Review.
-
Ongoing burden of disease and mortality from HIV/CMV coinfection in Africa in the antiretroviral therapy era.Front Microbiol. 2015 Sep 24;6:1016. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2015.01016. eCollection 2015. Front Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 26441939 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome in HIV infection: taking the bad with the good.Oral Dis. 2017 Oct;23(7):822-827. doi: 10.1111/odi.12606. Epub 2016 Dec 23. Oral Dis. 2017. PMID: 27801977 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Increased frequency and quantity of mucosal and plasma cytomegalovirus replication among Ugandan Adults Living with HIV.PLoS One. 2023 Aug 4;18(8):e0287516. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0287516. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 37540676 Free PMC article.
-
Cytomegalovirus and HIV: A Dangerous Pas de Deux.J Infect Dis. 2016 Oct 1;214 Suppl 2(Suppl 2):S67-74. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiw217. J Infect Dis. 2016. PMID: 27625433 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cytomegalovirus and paediatric HIV infection.J Virus Erad. 2016 Oct 5;2(4):208-214. doi: 10.1016/S2055-6640(20)30873-6. J Virus Erad. 2016. PMID: 27781102 Free PMC article.
-
Maternal Highly Active Antiretroviral Therapy Reduces Vertical Cytomegalovirus Transmission But Does Not Reduce Breast Milk Cytomegalovirus Levels.AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 2017 Apr;33(4):332-338. doi: 10.1089/AID.2016.0121. Epub 2016 Dec 6. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 2017. PMID: 27796131 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Schoenfisch AL, Dollard SC, Amin M, et al. Cytomegalovirus (CMV) shedding is highly correlated with markers of immunosuppression in CMV-seropositive women. J Med Microbiol 2011; 60:768–74. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 7-UM1 AI068636-07/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- 1K23AI093152-01A1/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AI027763/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000100/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN261200800001C/RC/CCR NIH HHS/United States
- K24 AI100665/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R24AI106039/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI-30731-19/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- T32AI102623/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- K23 AI093152/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AI030731/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AI036214/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- T32 AI102623/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI100665/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN261200800001E/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1TR000100/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- P30-AI027763/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI068636/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R24 AI106039/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States

