MRI evaluation and safety in the developing brain
- PMID: 25743582
- PMCID: PMC4380813
- DOI: 10.1053/j.semperi.2015.01.002
MRI evaluation and safety in the developing brain
Abstract
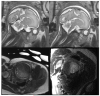
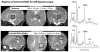
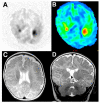
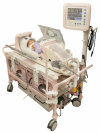
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) evaluation of the developing brain has dramatically increased over the last decade. Faster acquisitions and the development of advanced MRI sequences, such as magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS), diffusion tensor imaging (DTI), perfusion imaging, functional MR imaging (fMRI), and susceptibility-weighted imaging (SWI), as well as the use of higher magnetic field strengths has made MRI an invaluable tool for detailed evaluation of the developing brain. This article will provide an overview of the use and challenges associated with 1.5-T and 3-T static magnetic fields for evaluation of the developing brain. This review will also summarize the advantages, clinical challenges, and safety concerns specifically related to MRI in the fetus and newborn, including the implications of increased magnetic field strength, logistics related to transporting and monitoring of neonates during scanning, and sedation considerations, and a discussion of current technologies such as MRI conditional neonatal incubators and dedicated small-foot print neonatal intensive care unit (NICU) scanners.
Keywords: MR compatible incubator; MR spectroscopy; NICU magnet; arterial spin label perfusion; fetal MR; neonatal MRI.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- US Department of Health and Human Services. Food and Drug Administration. Center for Devices and Radiological Health Criteria for Significant Risk Investigations of Magnetic Resonance Diagnostic Devices - Guidance for Industry and Food and Drug Administration Staff [Internet] 2014 [cited 2014 Sep 3]. Available from: http://www.fda.gov/MedicalDevices/DeviceRegulationandGuidance/GuidanceDo....
-
- Arthur R. Magnetic resonance imaging in preterm infants. Pediatr Radiol. 2006 Jul;36(7):593–607. - PubMed
-
- Van Wezel-Meijler G, Steggerda SJ, Leijser LM. Cranial ultrasonography in neonates: role and limitations. Semin Perinatol. 2010 Feb;34(1):28–38. - PubMed
-
- Miller SP, Ferriero DM, Leonard C, Piecuch R, Glidden DV, Partridge JC, et al. Early brain injury in premature newborns detected with magnetic resonance imaging is associated with adverse early neurodevelopmental outcome. J Pediatr. 2005 Nov;147(5):609–16. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

