miR-663 attenuates tumor growth and invasiveness by targeting eEF1A2 in pancreatic cancer
- PMID: 25744894
- PMCID: PMC4332743
- DOI: 10.1186/s12943-015-0315-3
miR-663 attenuates tumor growth and invasiveness by targeting eEF1A2 in pancreatic cancer
Retraction in
-
Retraction Note: miR-663 attenuates tumor growth and invasiveness by targeting eEF1A2 in pancreatic cancer.Mol Cancer. 2019 Jul 18;18(1):118. doi: 10.1186/s12943-019-1042-y. Mol Cancer. 2019. PMID: 31319848 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Background: miR-663 is associated with many important biologic processes, such as the evolution, development, viral infection, inflammatory response, and carcinogenesis among vertebrates. However, the molecular function and mechanism of miR-663 in pancreatic cancer growth and invasion is still unclear.
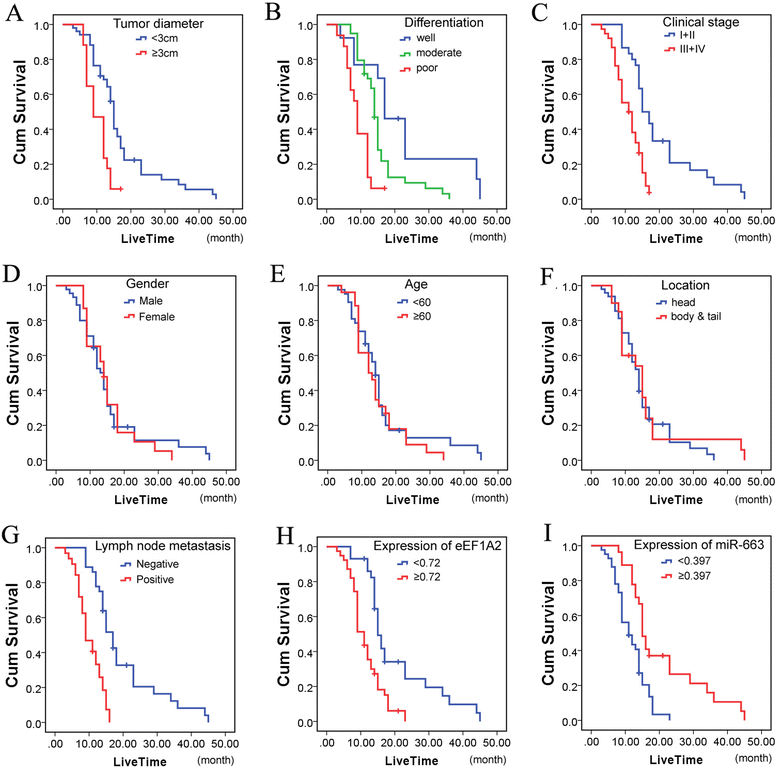
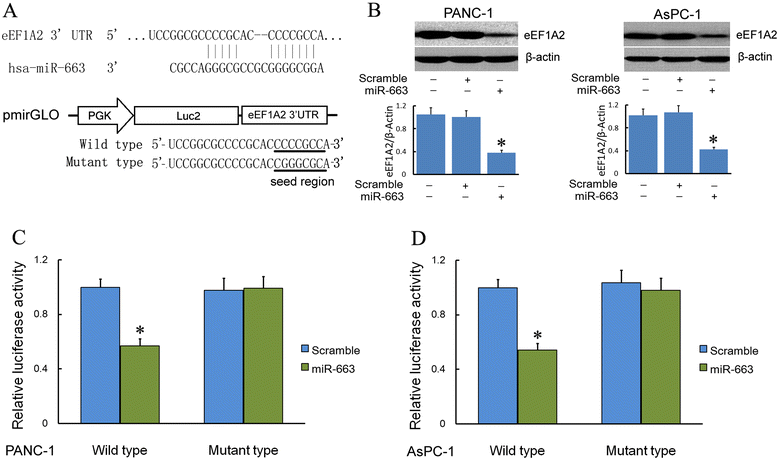
Methods: Western blot and real-time PCR were used to study the expression level of eEF1A2 protein and miR-663 in pancreatic cancer tissues and cell lines. The Pearson χ (2) test was used to determine the correlation between miR-663 expression and clinicopathologic features of patients. Patients' survival was analyzed using the Kaplan-Meier method, using the log-rank test for comparison. The biological function of miR-663 was examined by measuring cell growth, cell invasion and apoptosis analysis in vitro and in vivo. miR-663 target gene and signaling pathway was identified by luciferase activity assay and western blot.
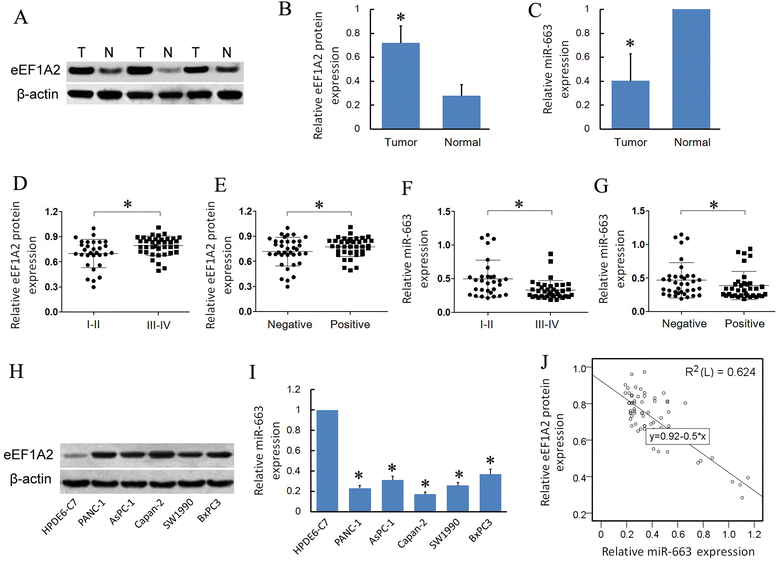
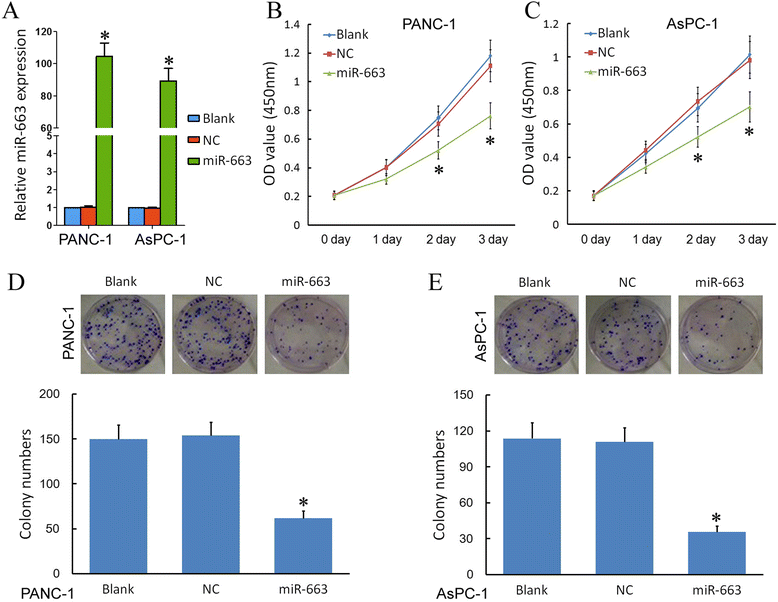
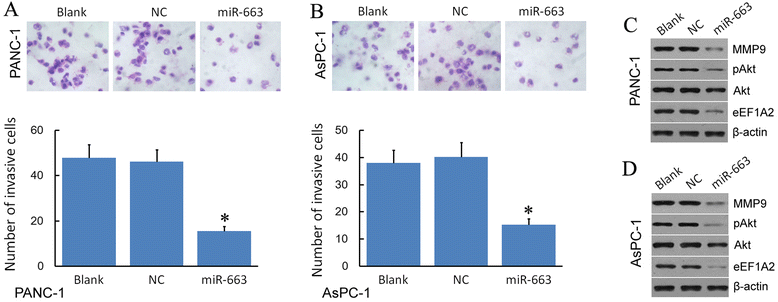
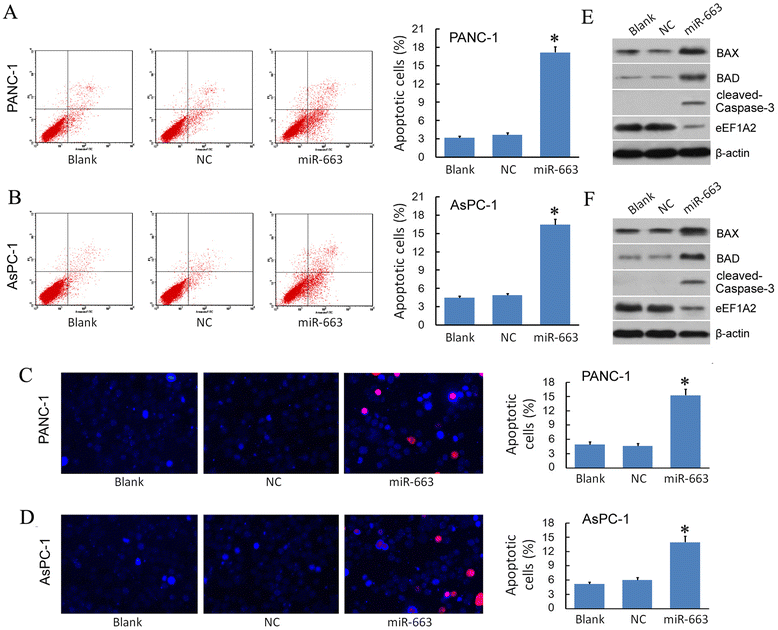
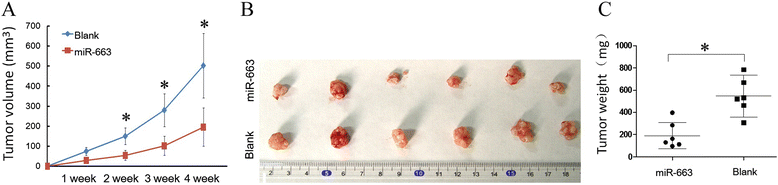
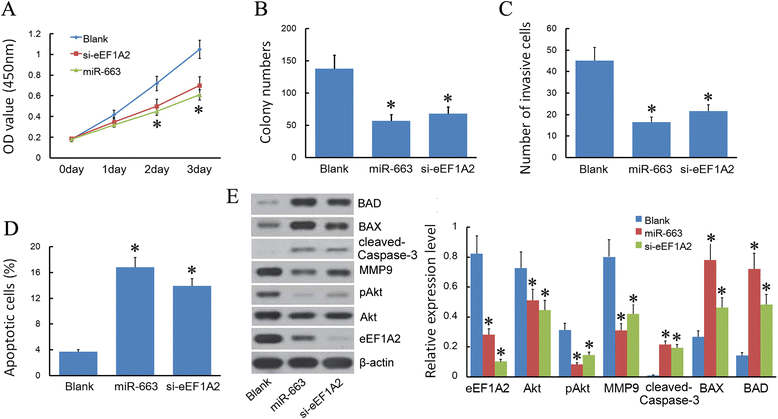
Results: We found that, in pancreatic cancer, eEF1A2 was significantly upregulated but miR-663 was significantly downregulated. Further results showed that the expression level of eEF1A2 and miR-663 was strongly associated with TNM stage and node metastasis status of the patients. miR-663 and eEF1A2 were inversely correlated with each other, and the changes in the expression levels of each can also predict the survival of patients with pancreatic cancer. We identified miR-663 as a tumor attenuate molecular that attenuated the proliferation and invasion of pancreatic cancer cells both in vitro and in vivo. Finally, we confirmed that the expression of eEF1A2 can partially restore the pro-apoptotic and anti-invasion functions of miR-663.
Conclusions: miR-663 attenuated the proliferation and invasion of pancreatic cells both in vitro and in vivo by directly targeting eEF1A2. miR-663 and eEF1A2 might be potential targets for the treatment of pancreatic cancer in the future.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

