Dialysis Modalities and HDL Composition and Function
- PMID: 25745027
- PMCID: PMC4552105
- DOI: 10.1681/ASN.2014030309
Dialysis Modalities and HDL Composition and Function
Abstract
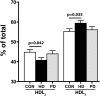
Lipid abnormalities may have an effect on clinical outcomes of patients on dialysis. Recent studies have indicated that HDL dysfunction is a hallmark of ESRD. In this study, we compared HDL composition and metrics of HDL functionality in patients undergoing hemodialysis (HD) or peritoneal dialysis (PD) with those in healthy controls. We detected a marked suppression of several metrics of HDL functionality in patients on HD or PD. Compositional analysis revealed that HDL from both dialysis groups shifted toward a more proinflammatory phenotype with profound alterations in the lipid moiety and protein composition. With regard to function, cholesterol efflux and anti-inflammatory and antiapoptotic functions seemed to be more severely suppressed in patients on HD, whereas HDL-associated paraoxonase activity was lowest in patients on PD. Quantification of enzyme activities involved in HDL metabolism suggested that HDL particle maturation and remodeling are altered in patients on HD or PD. In summary, our study provides mechanistic insights into the formation of dysfunctional HDL in patients with ESRD who are on HD or PD.
Keywords: cardiovascular disease; hemodialysis; lipids; peritoneal dialysis.
Copyright © 2015 by the American Society of Nephrology.
Figures



References
-
- Go AS, Chertow GM, Fan D, McCulloch CE, Hsu CY: Chronic kidney disease and the risks of death, cardiovascular events, and hospitalization. N Engl J Med 351: 1296–1305, 2004 - PubMed
-
- Burkart J: Metabolic consequences of peritoneal dialysis. Semin Dial 17: 498–504, 2004 - PubMed
-
- Garibotto G, Bonanni A, Verzola D: Effect of kidney failure and hemodialysis on protein and amino acid metabolism. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care 15: 78–84, 2012 - PubMed
-
- Gordon T, Castelli WP, Hjortland MC, Kannel WB, Dawber TR: High density lipoprotein as a protective factor against coronary heart disease. The Framingham Study. Am J Med 62: 707–714, 1977 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

