Mode of action of nintedanib in the treatment of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
- PMID: 25745043
- PMCID: PMC4416110
- DOI: 10.1183/09031936.00174914
Mode of action of nintedanib in the treatment of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
Abstract
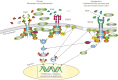
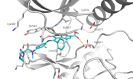
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) is a progressive and ultimately fatal disease characterised by fibrosis of the lung parenchyma and loss of lung function. Although the pathogenic pathways involved in IPF have not been fully elucidated, IPF is believed to be caused by repetitive alveolar epithelial cell injury and dysregulated repair, in which there is uncontrolled proliferation of lung fibroblasts and differentiation of fibroblasts into myofibroblasts, which excessively deposit extracellular matrix (ECM) proteins in the interstitial space. A number of profibrotic mediators including platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF), fibroblast growth factor (FGF) and transforming growth factor-β are believed to play important roles in the pathogenesis of IPF. Nintedanib is a potent small molecule inhibitor of the receptor tyrosine kinases PDGF receptor, FGF receptor and vascular endothelial growth factor receptor. Data from in vitro studies have shown that nintedanib interferes with processes active in fibrosis such as fibroblast proliferation, migration and differentiation, and the secretion of ECM. In addition, nintedanib has shown consistent anti-fibrotic and anti-inflammatory activity in animal models of lung fibrosis. These data provide a strong rationale for the clinical efficacy of nintedanib in patients with IPF, which has recently been demonstrated in phase III clinical trials.
Copyright ©ERS 2015.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: Disclosures can be found alongside the online version of this article at
Figures


References
-
- Vancheri C, Failla M, Crimi N, et al. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: a disease with similarities and links to cancer biology. Eur Respir J 2010; 35: 496–504. - PubMed
-
- Richeldi L, Cottin V, Flaherty KR, et al. Design of the INPULSIS™ trials: two phase 3 trials of nintedanib in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Respir Med 2014; 108: 1023–1030. - PubMed
-
- Richeldi L, du Bois RM, Raghu G, et al. Efficacy and safety of nintedanib in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. N Engl J Med 2014; 370: 2071–2082. - PubMed
-
- American Thoracic Society, European Respiratory Society. American Thoracic Society/European Respiratory Society International Multidisciplinary Consensus Classification of the Idiopathic Interstitial Pneumonias. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2002; 165: 277–304. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
