A new clinical scoring system for adenoid hypertrophy in children
- PMID: 25745612
- PMCID: PMC4344975
A new clinical scoring system for adenoid hypertrophy in children
Abstract
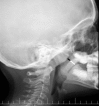
Introduction: Chronic nasal obstruction due to adenoid hypertrophy is a very common disorder. Although the clinical assessment of adenoid hypertrophy is essential, its real value in young children is difficult to evaluate. The purpose of this prospective study was to validate a simple clinical score to predict the severity of adenoid obstruction and to evaluate the relationship between this method of clinical scoring with radiography and nasopharyngeal endoscopy.
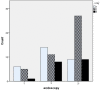
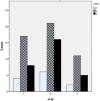
Materials and methods: Ninety symptomatic children were enrolled into this study. The clinical score included difficulty of breathing during sleep, apnea, and snoring. We investigated the relationship between clinical scoring, nasal endoscopy, and radiographic findings.
Results: The clinical score correlated very well with endoscopic findings (P<0.000), but the correlation between the clinical score and radiologic findings (P>0.05) and endoscopic findings and imaging (P>0.05) was weak.
Conclusion: Clinical findings could be used to select children for adenoidectomy, especially when endoscopic examination is not available or cannot be performed.
Keywords: Adenoids; Endoscopy; Radiography; Signs and symptoms; Sleep apnea syndromes; Snoring.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Modified adenoid grading system for evaluating adenoid size in children: a prospective validation study.Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2021 Jun;278(6):2147-2153. doi: 10.1007/s00405-021-06768-8. Epub 2021 Apr 2. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2021. PMID: 33797600
-
Lateral neck radiography versus direct video rhinoscopy in assessing adenoid size.J Otolaryngol. 2004 Dec;33(6):360-5. doi: 10.2310/7070.2004.03074. J Otolaryngol. 2004. PMID: 15971651
-
A suggested clinical score to predict the severity of adenoid obstruction in children.Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2006 Oct;263(10):924-8. doi: 10.1007/s00405-006-0086-y. Epub 2006 Jun 24. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2006. PMID: 16799801
-
[The tonsils and adenoids as a site of infection and the cause of obstruction].Pediatr Med Chir. 1998 Jul-Aug;20(4):237-47. Pediatr Med Chir. 1998. PMID: 9866845 Review. Italian.
-
Can adenoidal hypertrophy be treated with intranasal steroids?Rev Recent Clin Trials. 2010 May;5(2):123-7. doi: 10.2174/157488710791233590. Rev Recent Clin Trials. 2010. PMID: 20199384 Review.
Cited by
-
Adenotonsillar Hypertrophy and Cardiopulmonary Status: A Correlative Study.Cureus. 2022 Nov 6;14(11):e31175. doi: 10.7759/cureus.31175. eCollection 2022 Nov. Cureus. 2022. PMID: 36483896 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative evaluation of the upper pharyngeal airway among children with/without UCLP and with/without OSA.Sleep Breath. 2024 Nov 30;29(1):37. doi: 10.1007/s11325-024-03195-x. Sleep Breath. 2024. PMID: 39614951
-
Clinical outcome of Montelukast Sodium in Children with Adenoid Hypertrophy.Pak J Med Sci. 2021 Mar-Apr;37(2):362-366. doi: 10.12669/pjms.37.2.2670. Pak J Med Sci. 2021. PMID: 33679914 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of adenoid size in lateral radiographic, pathologic, and endoscopic measurements.Electron Physician. 2018 Jun 25;10(6):6935-6941. doi: 10.19082/6935. eCollection 2018 Jun. Electron Physician. 2018. PMID: 30034661 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of preoperative and postoperative cardiac function in children with adenotonsillar hypertrophy: a prospective cohort study.Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2022 Jun;279(6):3013-3019. doi: 10.1007/s00405-022-07255-4. Epub 2022 Jan 12. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2022. PMID: 35022863
References
-
- Mlynarek A, Tewfik MA, Hager A, Manoukian JJ, Schloss FMD, Tewfik FTL, et al. Lateral neck radiography versus direct video rhinoscopy in assessing adenoid size. J Otolaryngol. 2004;33(6):360–5. - PubMed
-
- Saedi B, Sadeghi M, Mojtahedi M, Mahboubi H. Diagnostic efficacy of different methods in the assessment of adenoid hypertrophy. Am J Otolaryngol. 2011;32(2):147–51. - PubMed
-
- Lertsburapa K, Schroeder JW, Sullivan C. Assessment of adenoid size: A comparison of lateral radiographic measurements, radiologist assessment, and nasal endoscopy. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2010;74(11):1281–5. - PubMed
-
- Brouilette R, Hanson D, David R, Klemka L, Anna S, Fernbach S, et al. A diagnostic approach to suspected obstructive sleep apnea in children. J Pediatr. 1984;105(1):10–14. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
