p21(WAF1/CIP1) RNA expression in highly HIV-1 exposed, uninfected individuals
- PMID: 25746435
- PMCID: PMC4352077
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0119218
p21(WAF1/CIP1) RNA expression in highly HIV-1 exposed, uninfected individuals
Abstract
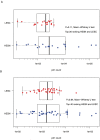
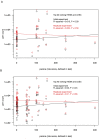
Some individuals remain HIV-1 antibody and PCR negative after repeated exposures to the virus, and are referred to as HIV-exposed seronegatives (HESN). However, the causes of resistance to HIV-1 infection in cases other than those with a homozygous CCR5Δ32 deletion are unclear. We hypothesized that human p21WAF1/CIP1 (a cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor) could play a role in resistance to HIV-1 infection in HESN, as p21 expression has been associated with suppression of HIV-1 in elite controllers and reported to block HIV-1 integration in cell culture. We measured p21 RNA expression in PBMC from 40 HESN and 40 low exposure HIV-1 seroconverters (LESC) prior to their infection using a real-time PCR assay. Comparing the 20 HESN with the highest exposure risk (median = 111 partners/2.5 years prior to the 20 LESC with the lowest exposure risk (median = 1 partner/2.5 years prior), p21 expression trended higher in HESN in only one of two experiments (P = 0.11 vs. P = 0.80). Additionally, comparison of p21 expression in the top 40 HESN (median = 73 partners/year) and lowest 40 LESC (median = 2 partners/year) showed no difference between the groups (P = 0.84). There was a weak linear trend between risk of infection after exposure and increasing p21 gene expression (R2 = 0.02, P = 0.12), but again only in one experiment. Hence, if p21 expression contributes to the resistance to viral infection in HESN, it likely plays a minor role evident only in those with extremely high levels of exposure to HIV-1.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Kaslow RA, Dorak T, Tang JJ (2005) Influence of host genetic variation on susceptibility to HIV type 1 infection. J Infect Dis 191 Suppl 1: S68–77. - PubMed
-
- Dean M, Carrington M, Winkler C, Huttley GA, Smith MW, et al. (1996) Genetic restriction of HIV-1 infection and progression to AIDS by a deletion allele of the CKR5 structural gene. Hemophilia Growth and Development Study, Multicenter AIDS Cohort Study, Multicenter Hemophilia Cohort Study, San Francisco City Cohort, ALIVE Study. Science 273: 1856–1862. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- U01 AI035042/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01-AI35040/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01-AI35042/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI035041/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AI057005/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01-AI35039/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI035040/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI035039/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1-AI35043/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30 MH058107/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI035043/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01-AI35041/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R37-047734/PHS HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

