TH9 cells are required for tissue mast cell accumulation during allergic inflammation
- PMID: 25746972
- PMCID: PMC4530056
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jaci.2015.01.021
TH9 cells are required for tissue mast cell accumulation during allergic inflammation
Abstract
Background: IL-9 is important for the growth and survival of mast cells. IL-9 is produced by T cells, natural killer T cells, mast cells, eosinophils, and innate lymphoid cells, although the cells required for mast cell accumulation during allergic inflammation remain undefined.
Objective: We sought to elucidate the role of TH9 cells in promoting mast cell accumulation in models of allergic lung inflammation.
Methods: Adoptive transfer of ovalbumin-specific TH2 and TH9 cells was used to assess the ability of each subset to mediate mast cell accumulation in tissues. Mast cell accumulation was assessed in wild-type mice and mice with PU.1-deficient T cells subjected to acute and chronic models of allergic inflammation.
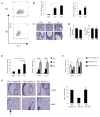
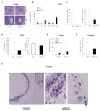
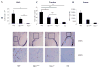
Results: Adoptive transfer experiments demonstrated that recipients of TH9 cells had significantly higher mast cell accumulation and expression of mast cell proteases compared with control or TH2 recipients. Mast cell accumulation was dependent on IL-9, but not IL-13, a cytokine required for many aspects of allergic inflammation. In models of acute and chronic allergic inflammation, decreased IL-9 levels in mice with PU.1-deficient T cells corresponded to diminished tissue mast cell numbers and expression of mast cell proteases. Mice with PU.1-deficient T cells have defects in IL-9 production from CD4(+) T cells, but not natural killer T cells or innate lymphoid cells, suggesting a TH cell-dependent phenotype. Rag1(-/-) mice subjected to a chronic model of allergic inflammation displayed reduced mast cell infiltration comparable with accumulation in mice with PU.1-deficient T cells, emphasizing the importance of IL-9 produced by T cells in mast cell recruitment.
Conclusion: TH9 cells are a major source of IL-9 in models of allergic inflammation and play an important role in mast cell accumulation and activation.
Keywords: PU.1; T(H)2 cells; T(H)9 cells; allergic inflammation; mast cells.
Copyright © 2015 American Academy of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Erpenbeck VJ, Hohlfeld JM, Volkmann B, Hagenberg A, Geldmacher H, Braun A, et al. Segmental allergen challenge in patients with atopic asthma leads to increased IL-9 expression in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid lymphocytes. The Journal of allergy and clinical immunology. 2003 Jun;111(6):1319–27. - PubMed
-
- Shimbara A, Christodoulopoulos P, Soussi-Gounni A, Olivenstein R, Nakamura Y, Levitt RC, et al. IL-9 and its receptor in allergic and nonallergic lung disease: increased expression in asthma. The Journal of allergy and clinical immunology. 2000 Jan;105(1 Pt 1):108–15. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

