Phase transition of a disordered nuage protein generates environmentally responsive membraneless organelles
- PMID: 25747659
- PMCID: PMC4352761
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2015.01.013
Phase transition of a disordered nuage protein generates environmentally responsive membraneless organelles
Abstract
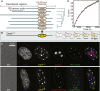
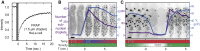
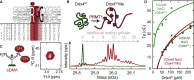
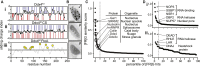
Cells chemically isolate molecules in compartments to both facilitate and regulate their interactions. In addition to membrane-encapsulated compartments, cells can form proteinaceous and membraneless organelles, including nucleoli, Cajal and PML bodies, and stress granules. The principles that determine when and why these structures form have remained elusive. Here, we demonstrate that the disordered tails of Ddx4, a primary constituent of nuage or germ granules, form phase-separated organelles both in live cells and in vitro. These bodies are stabilized by patterned electrostatic interactions that are highly sensitive to temperature, ionic strength, arginine methylation, and splicing. Sequence determinants are used to identify proteins found in both membraneless organelles and cell adhesion. Moreover, the bodies provide an alternative solvent environment that can concentrate single-stranded DNA but largely exclude double-stranded DNA. We propose that phase separation of disordered proteins containing weakly interacting blocks is a general mechanism for forming regulated, membraneless organelles.
Copyright © 2015 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures




Comment in
-
Mapping from sequence to droplets.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2021 Mar;22(3):163. doi: 10.1038/s41580-021-00333-1. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2021. PMID: 33473198 No abstract available.
References
-
- Baldwin A.J., Knowles T.P., Tartaglia G.G., Fitzpatrick A.W., Devlin G.L., Shammas S.L., Waudby C.A., Mossuto M.F., Meehan S., Gras S.L. Metastability of native proteins and the phenomenon of amyloid formation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011;133:14160–14163. - PubMed
-
- Brangwynne C.P. Soft active aggregates: mechanics, dynamics and self-assembly of liquid-like intracellular protein bodies. Soft Matter. 2011;7:3052–3059.
-
- Brangwynne C.P., Eckmann C.R., Courson D.S., Rybarska A., Hoege C., Gharakhani J., Jülicher F., Hyman A.A. Germline P granules are liquid droplets that localize by controlled dissolution/condensation. Science. 2009;324:1729–1732. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

