Myocardial autophagic energy stress responses--macroautophagy, mitophagy, and glycophagy
- PMID: 25747748
- PMCID: PMC4436984
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpheart.00002.2015
Myocardial autophagic energy stress responses--macroautophagy, mitophagy, and glycophagy
Abstract
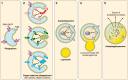
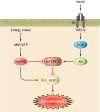
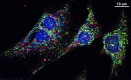
An understanding of the role of autophagic processes in the management of cardiac metabolic stress responses is advancing rapidly and progressing beyond a conceptualization of the autophagosome as a simple cell recycling depot. The importance of autophagy dysregulation in diabetic cardiomyopathy and in ischemic heart disease - both conditions comprising the majority of cardiac disease burden - has now become apparent. New findings have revealed that specific autophagic processes may operate in the cardiomyocyte, specialized for selective recognition and management of mitochondria and glycogen particles in addition to protein macromolecular structures. Thus mitophagy, glycophagy, and macroautophagy regulatory pathways have become the focus of intensive experimental effort, and delineating the signaling pathways involved in these processes offers potential for targeted therapeutic intervention. Chronically elevated macroautophagic activity in the diabetic myocardium is generally observed in association with structural and functional cardiomyopathy; yet there are also numerous reports of detrimental effect of autophagy suppression in diabetes. Autophagy induction has been identified as a key component of protective mechanisms that can be recruited to support the ischemic heart, but in this setting benefit may be mitigated by adverse downstream autophagic consequences. Recent report of glycophagy upregulation in diabetic cardiomyopathy opens up a novel area of investigation. Similarly, a role for glycogen management in ischemia protection through glycophagy initiation is an exciting prospect under investigation.
Keywords: autophagy; cardiac; cardiomyocyte; diabetes; heart; ischemia.
Copyright © 2015 the American Physiological Society.
Figures


References
-
- Alfarano C, Suffredini S, Fantappie O, Mugelli A, Cerbai E, Manni ME, Raimondi L. The effect of losartan treatment on the response of diabetic cardiomyocytes to ATP depletion. Pharmacol Res 63: 225–232, 2011. - PubMed
-
- Chou IP, Chiu YP, Ding ST, Liu BH, Lin YY, Chen CY. Adiponectin receptor 1 overexpression reduces lipid accumulation and hypertrophy in the heart of diet-induced obese mice—possible involvement of oxidative stress and autophagy. Endocr Res 39: 173–179, 2014. - PubMed
-
- Cross HR, Opie LH, Radda GK, Clarke K. Is a high glycogen content beneficial or detrimental to the ischemic rat heart? A controversy resolved. Circ Res 78: 482–491, 1996. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

